In today’s digital era, businesses across various industries, such as logistics, navigation, retail, telecommunications, and urban planning, face the critical challenge of maintaining accurate location data. Accurate location data is vital for optimizing operations, enhancing customer experiences, and making informed decisions. But why is this so crucial for your business, and what impact can it have?
In this article, we’ll delve into location data accuracy. We’ll explore why it’s so essential, the challenges that come with it, and practical solutions to enhance data precision.
Whether you’re a data scientist, a marketer, or a logistics manager, this guide will provide you with the insights you need to leverage accurate location data for your business. Let’s go!
Without accurate location data, numerous problems arise
- Logistics companies experience delayed deliveries and increased costs due to incorrect addresses
- In navigation services, users receive poor directions, leading to frustration and decreased trust
- Retail businesses misallocate resources, resulting in stock shortages or overstocking in the wrong locations
- Telecommunications companies struggle with network planning and optimization, causing service disruptions
- Urban planners face challenges in infrastructure development, leading to inefficient public services and dissatisfied residents
Accurate location data is essential to avoid these issues and ensure smooth, efficient operations across various industries.
But here’s the catch – ensuring the accuracy of location data is no small feat. Are you aware of the challenges businesses face in maintaining precise location data? The obstacles are numerous and complex, from inconsistent address formats across different countries to the dynamic nature of geographical changes.
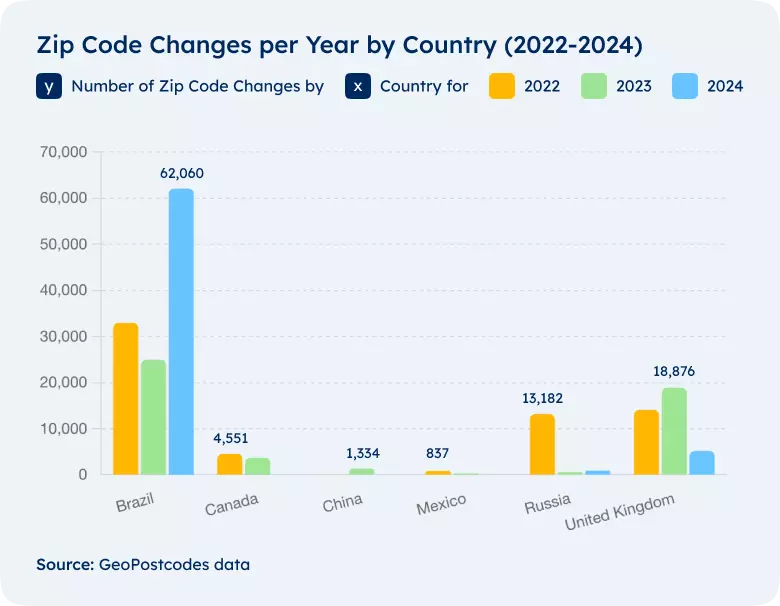
For example, authorities regularly update postal codes to reflect new developments, administrative changes, and population shifts.
They rename streets, develop new neighborhoods, and retire old addresses. You must continuously monitor and update your data to keep up with these changes.
Moreover, geographical and cultural variations further complicate the process. Obtaining accurate location data can be complex in some rural areas or regions with non-standard addressing systems. Add to this the variability of data sources – from government records to customer inputs – and the challenge of integrating these diverse datasets into a single, coherent database becomes evident.
💡 For over 15 years, we have created the most comprehensive worldwide zip code database. Our location data is updated weekly, relying on more than 1,500 sources. Browse GeoPostcodes datasets and download a free sample here.
Understanding Location Data Accuracy
Location data accuracy refers to the degree to which geographical information, such as addresses and coordinates, precisely matches the physical locations they represent.
It includes correctly mapping postal codes, street names, and geospatial coordinates. Accurate location data is essential for various applications, from delivering packages to targeted marketing campaigns.
Where Does Location Data Come from?
Creating location data involves capturing and mapping geographic information using various technologies and methods. This process starts with gathering raw data from GPS devices, mobile sensors, and satellite imagery.
After collecting this raw data, the next step is to process and refine it using algorithms.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a crucial role in this process. GIS technology helps manage, analyze, and visualize geographic data.
You can think of it as an intelligent map-making tool that can layer different types of information on a map, such as roads, population data, and environmental features. This layering helps you see and analyze patterns and relationships in the data.
There are two main types of location data: vector and raster. Vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to represent specific features. For instance, a point might mark a city, a line might show a road, and a polygon might outline a park.
On the other hand, Raster data consists of a grid of cells, similar to pixels in a digital photo. Each cell holds a value representing information, such as temperature or elevation, often derived from satellite images.
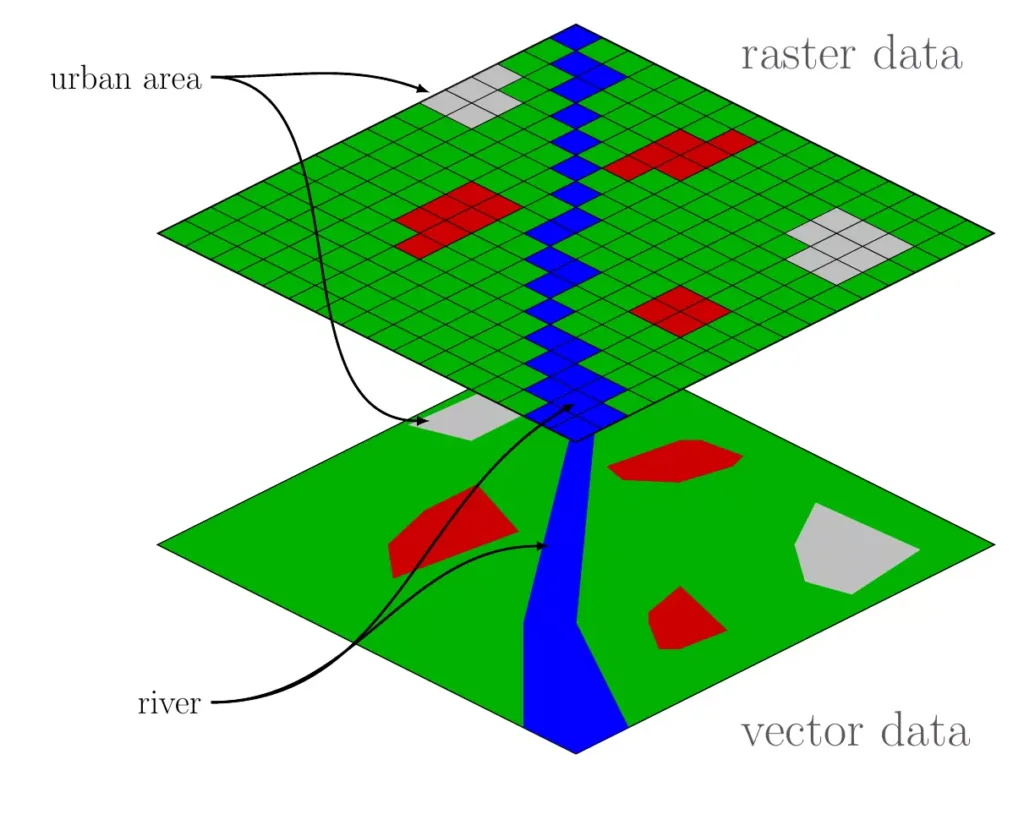
You can integrate various datasets into your GIS to enhance your maps and analyses. These datasets might include demographic statistics (like population density), business data (like store locations), and high-resolution imagery (like detailed aerial photos).
Integrating these datasets into GIS allows you to create detailed maps and perform spatial analysis. Spatial analysis involves examining the locations and relationships between different features on a map.
For example, you might analyze how close people live to a park or how traffic patterns change over time.
These technologies allow you to gain valuable insights into spatial patterns and trends, helping you make more informed and strategic decisions.
Whether involved in urban planning, environmental management, or marketing, understanding location data can significantly enhance your ability to analyze and solve problems.
The Steps of Location Data Creation
Data Collection: The initial step involves collecting raw geographical data. We do it through satellite imagery, GPS devices, and public records such as postal codes and addresses.
Data Processing: Once the raw data is collected, it is processed to remove any inaccuracies and inconsistencies. This step often involves geocoding, which converts addresses into geographical coordinates.
Data Integration: We integrate processed data into databases and mapping systems. This step ensures that we can access and analyze all location data coherently.
Data Verification: The integrated data is verified against multiple sources to ensure accuracy. It can involve cross-referencing with official records, using AI algorithms to detect anomalies and manual verification processes.
Data Maintenance: Location data is dynamic and requires regular updates. We add new addresses, remove old ones, and reflect changes in geographical boundaries in the data.
The Challenges of Achieving Accurate Location Data
Inconsistent Address Formats
Addresses can vary widely in format depending on the country, region, and even local conventions. For instance, a typical address in Japan will look very different from one in the United States or France. Variations may include differences in street names, building number assignments, and postal code structures. This complexity makes it challenging to standardize and verify address data accurately.

Geographic and Cultural Variations
Obtaining accurate location data can be complicated in rural areas or regions with non-standard addressing systems. Some rural areas might not have formal street names or house numbers, relying instead on local landmarks or descriptions.
Additionally, cultural differences in address formatting can complicate data integration efforts.
Data Entry Errors
Human errors during data entry can lead to significant inaccuracies. These errors can occur at any point in the data collection, from customers entering their addresses online to employees inputting data into systems.
Implementing automated data entry solutions and validation checks can help mitigate these errors.

Data Source Variability
Businesses often use location data from multiple sources, such as government records, commercial data providers, and customer inputs. Each source may have different formats, levels of detail, and accuracy. Integrating these diverse data sets into a single, coherent database requires sophisticated tools and methods to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Dynamic Nature of Location Data
Location data is not static. Postal authorities change postal codes, establish new streets, and rename old ones. Keeping up with these changes requires continuous data updates and validation.

The Cost of Inaccurate Data
Inaccurate location data can have significant financial impacts. For instance, incorrect delivery addresses can lead to failed deliveries, increased operational costs, and dissatisfied customers.
Targeting the wrong locations in marketing can result in wasted resources and missed opportunities. For emergency services, inaccuracies in location data can delay response times and potentially endanger lives.
The Journey to Accurate Location Data
Start with Geocoding
Geocoding is the process of converting addresses into geographical coordinates. This foundational step ensures that every address corresponds to the correct location on the map.
High-quality geocoding services can significantly improve the accuracy of your location data. You can work with a reliable provider, like GeoPostcodes, to handle geocoding.
Implement Data Cleansing and Standardization
Data cleansing involves identifying and correcting inaccuracies and inconsistencies in datasets. Standardizing address formats ensures uniformity, making managing and verifying location data easier. For instance, ensuring all addresses follow a consistent format can prevent errors and improve data integration.

Regular Data Updates
Given the dynamic nature of location data, regular updates are essential. It includes updating new addresses, postal codes, and other geographical changes. Businesses should establish processes for continuously monitoring and updating their location data to maintain accuracy.
Validation and Verification
Robust validation and verification processes are vital for maintaining the integrity of location data. These processes involve cross-referencing data with reliable sources and using algorithms to detect and correct errors.

Use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS technology is essential for managing and analyzing geographical data. It allows businesses to visualize, question, analyze, and interpret location data to understand relationships, patterns, and trends. Integrating GIS into your data management processes can significantly enhance the accuracy and usability of location data.
Practical Applications of Accurate Location Data
Logistics and Delivery
Accurate location data is essential for logistics companies. It ensures that packages are delivered to the correct addresses, reducing the likelihood of lost or delayed deliveries. It improves customer satisfaction and reduces operational costs.
Our accurate and reliable data at GeoPostcodes helps logistics companies optimize delivery routes and enhance efficiency.
For example, a logistics company can use precise location data to plan the most efficient delivery routes, taking into account traffic conditions, road closures, and delivery time windows. It ensures timely deliveries and reduces fuel consumption and vehicle wear and tear.
Marketing and Customer Engagement
Accurate location data enables businesses to execute targeted marketing campaigns. Companies can tailor their messages and offers to specific regions by understanding where their customers are, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
For example, a retail company can use accurate location data to send promotions to customers in a particular area, boosting local sales.
Emergency Services
In emergency services, location data accuracy can be a matter of life and death. Precise location data ensures that emergency responders can reach the scene quickly and efficiently. It is essential in densely populated urban areas or regions with complex addressing systems.
For instance, accurate location data can help emergency services pinpoint the exact location of an incident, ensuring a swift response. It can save lives and minimize damage in critical situations such as natural disasters, medical emergencies, and public safety incidents.
Fraud Prevention
Accurate location data can help prevent fraud. By verifying the authenticity of addresses and ensuring they match with other data points, businesses can reduce the risk of fraudulent activities. It is essential for financial institutions and e-commerce platforms.
For example, accurate location data can help verify the legitimacy of a customer’s address during online transactions, reducing the risk of fraudulent orders and chargebacks. It can enhance security and protect businesses from financial losses.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
Urban planners and government agencies use accurate location data to design and develop infrastructure projects.
Precise data helps plan road networks, public transportation routes, and utility services, ensuring efficient development and meeting the population’s needs.
For example, accurate location data can help urban planners identify areas with high traffic congestion and develop solutions to alleviate it.
It can also help plan new public transportation routes to meet the community’s needs and improve overall accessibility.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Data Integration
Integrating location data from various sources can be challenging. Ensuring data from different systems and formats is accurately combined requires meticulous planning and execution.
Businesses should use data integration tools and services that support multiple data formats and ensure seamless integration.
For example, integrating location data from public records, GPS devices, and customer databases can provide a comprehensive and accurate dataset. Advanced data integration tools can ensure consistency and accuracy across different data sources.
Data Privacy and Security
With increasing concerns over data privacy, ensuring location data security is paramount. Businesses must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive location information, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
For instance, implementing encryption protocols can help protect location data from unauthorized access.
Regular security audits help identify and address potential vulnerabilities, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
Addressing Geographical Complexities

Businesses must use advanced geospatial analysis and verification techniques to ensure accuracy in regions with sparse addressing or similar-sounding place names.
Satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS) can help validate and enhance location data in such areas.
For example, in rural areas with sparse addressing, satellite imagery can provide accurate geographical information, ensuring precise location data.
GIS technology can help visualize and analyze geographical data, providing deeper insights and enhancing data accuracy.
Managing Dynamic Location Data
Given the dynamic nature of location data, businesses must establish processes for continuously monitoring and updating their data.
It includes regularly updating new addresses, postal codes, and other geographical changes.
For instance, automated data update processes can help ensure that location data remains current and accurate. Regularly monitoring changes in geographical information can help businesses respond promptly to updates, maintaining data integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, accurate location data is crucial for modern business operations. It is the backbone of efficient logistics, precise navigation, targeted marketing, and effective urban planning.
Ensuring data accuracy mitigates the risks of costly errors, enhances customer satisfaction, and optimizes resource allocation. However, maintaining this accuracy is complex due to dynamic geographical changes, inconsistent address formats, and data entry errors.
By partnering with reliable data providers, businesses can significantly enhance the accuracy of their location data. At GeoPostcodes, we are committed to providing comprehensive and up-to-date location data, helping companies across various industries to achieve operational excellence.
💡 For over 15 years, we have created the most comprehensive worldwide zip code database. Our location data is updated weekly, relying on more than 1,500 sources. Browse GeoPostcodes datasets and download a free sample here.
Remember, accurate location data is a technical necessity and a strategic asset that can drive business success.
As we continue to navigate an increasingly digital world, the ability to manage and utilize precise location data will remain a critical factor in staying competitive and meeting the ever-evolving needs of customers and markets.
Explore our extensive datasets and discover how GeoPostcodes can help your business harness the power of accurate location data.
FAQ
How does Google Analytics location data work?
Google Analytics location data is collected primarily from the IP addresses of the devices that visit your website.
This data helps determine your users’ geographical locations, giving insights into where your traffic is coming from.
However, the accuracy of this data can vary depending on the quality of the IP-based geolocation services used by Google Analytics.
How is mobile location data collected and used?
Mobile location data comes from GPS, Wi-Fi, and mobile phone triangulation.
This data is used for navigation, location-based services, targeted marketing, and analytics. It is crucial for delivering precise services and insights.
What is the difference between actual location and GPS location?
Actual location refers to the real-world geographical position of a device or place.
On the other hand, GPS location is the location data obtained from the Global Positioning System, which uses satellites to determine precise coordinates.
While GPS location is typically very accurate, signal blockage and atmospheric conditions can sometimes affect it.
How does Google Maps determine location precision?
Google Maps determines location precision by combining GPS, Wi-Fi, cell tower signals, and user input. The app integrates these multiple data sources to provide the most accurate location possible.
Factors such as the quality of GPS signals, the density of Wi-Fi networks, and the number of nearby cell towers all contribute to the precision of Google Maps’ location data set.
How is location determined on mobile devices?
Location determined on mobile devices involves using multiple location signals such as GPS, Wi-Fi, and cell tower triangulation.
The device uses these signals to estimate its geographical position.
For instance, GPS provides accurate coordinates, while Wi-Fi and cell towers help in locations where GPS signals might be weak, such as indoors or in urban canyons.
Combining these signals ensures the best possible accuracy for the device’s location.
How does a device’s location affect location accuracy?
The device location is crucial for determining location accuracy.
Factors like GPS signal strength, network connectivity, and environmental conditions (such as tall buildings or dense forests) can impact the accuracy of the location data derived from a user’s device.
What is the role of a location signal in determining physical location?
A location signal, such as a GPS signal, Wi-Fi, or cell tower triangulation, plays a significant role in determining a physical location.
The strength and clarity of these signals directly affect the accuracy of the location data.
A robust and unobstructed signal generally results in more accurate location information.
How accurate is location data?
Location data accuracy varies based on the source and method used to gather the information. High-accuracy location data typically has a margin of error of a few meters.
However, this can be less precise when using methods like IP geolocation, which might only provide accuracy at the country—or city level.
Factors affecting location data accuracy include the quality of GPS signals, Wi-Fi network density, and proxy servers or VPNs that can obscure a user’s actual location.
How is location accuracy measured?
Location accuracy is measured by comparing the reported location to the actual physical location.
GPS accuracy is often described in terms of distance error. It is measured by how close the GPS coordinates are to the actual location, usually within a few meters.
Other methods, like Wi-Fi or cell tower triangulation, measure accuracy by the proximity of multiple signals to the proper location.
High-accuracy systems like RTLS (Real-Time Location Systems) can achieve sub-meter or even centimeter-level precision.
How do you check location accuracy?
To check location accuracy, you can compare the reported location data against a known, precise location location. It involves:
- Using GPS Devices: Check the GPS data against a mapped location
- Cross-referencing with Multiple Data Sources: Validate the location using different signals, such as Wi-Fi, cell towers, and GPS
- Implementing RTLS: Use systems that offer real-time, highly accurate tracking for critical applications
- Testing in Controlled Environments: Use environments where the actual location is known and compare it to the data reported by the device
What does location accuracy mean?
Location accuracy refers to the closeness of the measured location data to the actual geographical position. It encompasses two main concepts:
Accuracy: How close the measured location is to the proper location.
Precision is the consistency of repeated measurements. High precision means the data points are very close to each other, even if they are not accurate.
For instance, GPS coordinates with many decimal points indicate higher precision.
In practical terms, accuracy ensures that the location data is reliable for use in applications like navigation, logistics, and emergency services
By understanding these aspects and employing advanced technologies, businesses can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their location data, thereby improving operational efficiency and decision-making.




