Key Takeaways
- Pandemics and trade wars have spiked material costs and shortages
- Issues like port congestion and container shortages are pushing up costs and delays
- Reliable location data ensures precise deliveries and efficient route planning, keeping supply chains on track
- Leveraging digital tools and intelligent strategies boosts supply chain resilience
Introduction
The global supply chain faces numerous challenges that disrupt the smooth flow of goods and services. The lasting effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S.-China trade war, geopolitical tensions, labor shortages, equipment shortages, and environmental concerns have all made these issues worse.
These challenges bring risks and opportunities for businesses, consumers, and policymakers.
This article will examine the causes of these global supply chain challenges, the strategies, and innovations used to tackle them and explore the future.
We’ll also provide practical advice and insights to help you navigate the complexities and uncertainties of the global supply chain landscape.
Unraveling the Knots: Identifying Core Challenges
The key issues that significantly impact supply chain efficiency, resilience, and sustainability include:
Material Scarcity and Increased Costs

The smooth operation of global supply chains depends heavily on the consistent availability and affordability of raw materials and intermediate goods.
Unfortunately, trade conflicts, environmental policies, geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and pandemic-induced disruptions have caused shortages and rising prices of essential resources.
The trade standoff between the U.S. and China has led to tariffs and quotas on critical products like steel, aluminum, semiconductors, and rare earth metals, which are crucial for the manufacturing and tech industries.
The shift towards a low-carbon economy and growing environmental and social governance awareness have also pushed businesses to source materials ethically and sustainably, potentially increasing expenses and extending delivery times.
Logistical Hurdles: Port Congestion and Freight Challenges

Efficient movement of goods across borders and regions is crucial for the health of global supply chains.
However, the transport and logistics sector faces several challenges, including port congestion, container shortages, freight capacity limitations, labor disputes, and cyber threats. These issues have led to significant delays, disruptions, and increased shipping costs.
One notable event was the blockage of the Suez Canal in March 2021 by a large container ship, which caused a significant backlog of vessels and cargo, disrupting global trade and driving up shipping expenses.
Additionally, the pandemic-induced erratic demand for air and sea freight has caused imbalances in supply and demand and increased freight rate volatility.
Demand Forecasting and Consumer Shifts

Successfully predicting and adapting to consumer demands is vital for global supply chains.
The pandemic has altered lifestyles, impacting the demand for various products and services. For example, there has been a rise in demand for online shopping, home entertainment, and health and wellness products, while interest in travel, hospitality, and fashion has declined.
These shifts force businesses to recalibrate their production, inventory, and distribution strategies.
Additionally, expanding e-commerce and digital platforms has raised consumer expectations for faster, more cost-effective, personalized delivery services, pressuring supply chains to become more agile, flexible, and responsive.
Strategic Adaptations and Innovations
In today’s world, global supply chains must be proactive and innovative to overcome their challenges. They must implement strategic adaptations and innovations to enhance efficiency, agility, and resilience. Here are several critical steps to achieve these goals:
Embracing Digital Transformation

Digital technologies offer potent solutions for enhancing supply chain visibility, coordination, and optimization.
They enable real-time collection, analysis, and data communication across the supply network, improving the accuracy and timeliness of crucial processes like demand forecasting, inventory management, and order fulfillment.
Additionally, digital technologies foster collaboration and information sharing among all stakeholders in the supply chain, including partners, customers, and regulators.
It enhances trust and transparency and supports the development of new business models and capabilities, such as e-commerce, omnichannel distribution, and customization.
Technologies like cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, blockchain, and 5G are widely adopted or tested in global supply chains.
Reimagining Supply Chain Structures
The conventional global supply chain model, characterized by long-distance sourcing, centralized production, and lean inventories, has shown vulnerabilities to disruptions and uncertainties.
As a result, many businesses are reevaluating their supply chain structures and moving towards more adaptable and robust frameworks.
Strategies like nearshoring, reshoring, regionalization, diversification, and localization are being implemented or considered.
These approaches aim to reduce reliance on a single source or region, bring production closer to the point of consumption, and enhance responsiveness to local market needs and preferences.
However, these strategies have challenges, including higher costs, reduced economies of scale, and regulatory hurdles.
Building a Resilient Future
The main goal for global supply chains is to achieve resilience—the ability to endure, recover from, and adapt to adversities and changes.
Achieving resilience involves more than operational efficiency; it requires strategic foresight, innovation, and collaboration.
Global supply chains must invest in risk management, contingency planning, scenario analysis, and crisis response mechanisms to build a resilient future.
It’s essential to cultivate a culture of learning, experimentation, and continuous improvement while leveraging insights and opportunities from both current and past crises.
Additionally, aligning supply chain objectives and practices with broader societal goals and values, such as sustainability, inclusivity, and responsibility, is crucial.
Proactive Measures and Predictions
The future of global supply chains is uncertain, influenced by the ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S.-China trade war, and various geopolitical and environmental issues.
Global supply chains must balance immediate adjustments with long-term strategic goals to endure and excel in these challenging times.
Embracing proactive steps to safeguard their operations is crucial. Here are essential strategies:
Short-term Adjustments vs. Long-Term Strategy
Global supply chains must adapt quickly to immediate challenges and disruptions. This might involve increasing stock levels, finding alternative suppliers, renegotiating contracts, adjusting pricing, and boosting logistics efficiency.
💡 Use accurate location data to plan efficient routes, reduce transit times and fuel costs, and minimize delivery errors. Our location data is updated weekly and relies on more than 1,500 sources. Browse GeoPostcodes datasets and download a free sample here.
However, these short-term actions mustn’t distract from long-term strategies. These strategies should evolve to meet the changing demands of consumers, stakeholders, and society.
Additionally, global supply chains can use insights from current crises to strengthen their long-term capabilities and competitive edge.
It can be achieved by adopting digital technologies to enhance efficiency, agility, and resilience and by implementing sustainable and ethical practices to reduce environmental and social impacts.
Future-Proofing Supply Chains
To effectively prepare for the future, global supply chains must anticipate and mitigate risks from market volatility, regulatory changes, technological advances, and natural disasters.
Equally important is the ability to capitalize on emerging trends, customer preferences, and competitive advantages.
It requires a comprehensive, forward-thinking approach that considers various scenarios, integrates continuous feedback, and promotes learning.
Building a trustworthy collaborative environment among partners, customers, and regulators is essential. It encourages a shared effort in devising solutions and generating value. Key predictions and strategies for enhancing the resilience and sustainability of global supply chains include:
- Increasing regionalization and diversification will decrease reliance on single sources or markets and better meet local customers’ specific needs and preferences.
- Expanding digitalization and automation by adopting cutting-edge technologies like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and 5G, which enhance visibility, coordination, and operational efficiency.
- Emphasizing sustainability and responsibility by aligning business goals with societal environmental and social objectives, such as those outlined in the UN Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement.
Role of Accurate Location Data in Mitigating Supply Chain Challenges
Accurate location data is one of the critical components for keeping supply chains running smoothly. Without it, companies face problems, from disrupted routes to delivery mistakes, like packages ending up at the wrong address or getting delayed because of poor route planning.
It allows businesses to plan better routes, reducing transit times and fuel costs. Plus, it improves scheduling to avoid port congestion and manage inventory by more accurately predicting delivery times.
Standardizing address data across different regions presents a significant challenge for businesses operating in multiple countries. Each country’s address format makes unifying data for global operations difficult.
For example, many companies struggle with China’s location data due to strict data protection policies, which make it difficult to access accurate information.
It poses a challenge when assigning customers to the correct depot, as precise location data is crucial to avoid errors like incorrect deliveries or inefficient route planning.
GeoPostcodes solves these issues by providing clean, accurate postal and boundary data for China, including up to 6-digit granularity of postal codes and additional latitude and longitude coordinates.
🌎 Searching for accurate China zip code format? Download our China zip code sample dataset here.
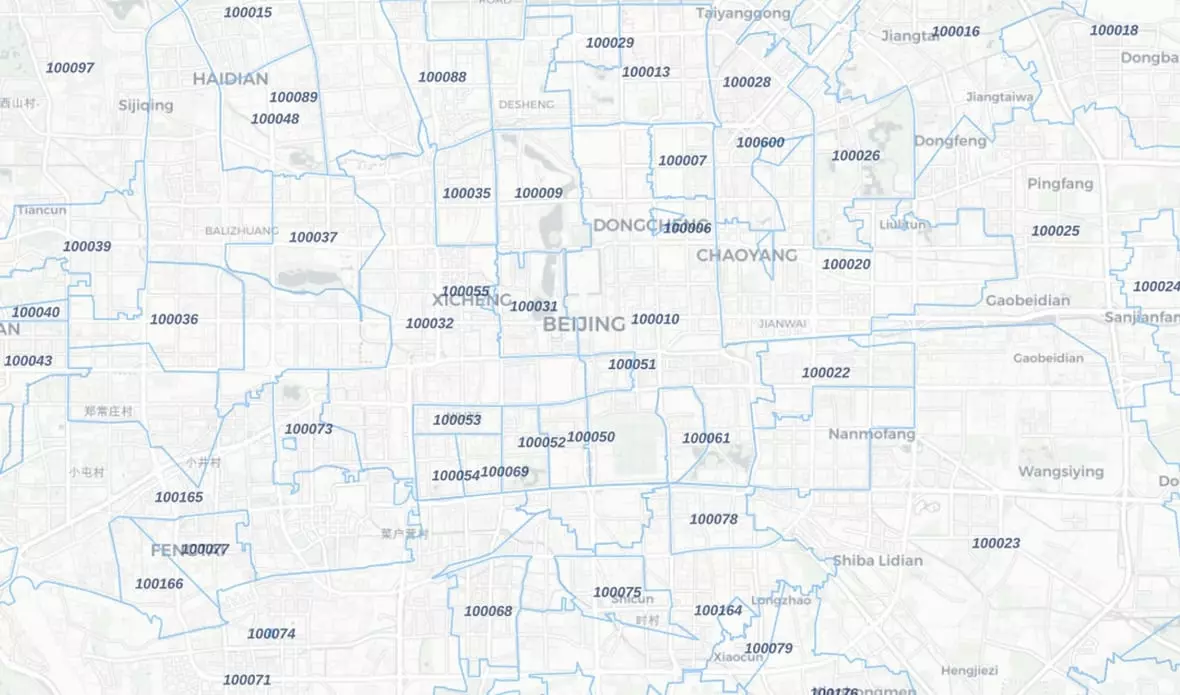
This detailed data supports advanced geospatial analysis and routing algorithms. Incorporating GeoPostcodes’ data helps businesses improve their routing strategies with precise distance measurements. These measurements can be combined with a drive-time approach, which calculates travel time between points using additional tools or services.
This method considers traffic conditions, road types, and speed limits, offering a more realistic and efficient route planning solution.
Conclusion
In the 21st century, global supply chains are navigating an era of unparalleled challenges and opportunities. These networks must adeptly handle the complexities and uncertainties of today’s global supply chain landscape while evolving and innovating to meet the changing demands and expectations of customers, stakeholders, and society.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the main challenges supply chains face, highlighted strategic adaptations and innovations, and outlined proactive steps and forecasts for the future of global supply networks.
One of the critical components in overcoming these challenges is accurate location data. At GeoPostcodes, we provide precise and reliable location data crucial for smooth supply chain operations.
Our data enables efficient route planning, reduces transit times and fuel costs, and minimizes delivery errors. It integrates seamlessly with GIS and ERP systems, enhancing location intelligence across supply chain operations.
We hope this discussion has offered valuable insights and practical advice for enhancing your global supply chain operations. To learn more about how GeoPostcodes can help your business thrive in these challenging times, explore our resources or contact us directly.
FAQ
What are the main challenges facing global supply chains?
The main challenges facing global supply chains include:
- Global friction and geopolitical tensions disrupt trade routes, creating uncertainty and instability
- Rising operational costs are driven by inflation and transportation, logistics, and supplier pricing increases
- Fluctuating demand and higher customer expectations necessitate agile and responsive supply chain management
- Labor shortages and skill gaps impact the availability and quality of human resources
- Sustainability pressures and environmental concerns call for more eco-friendly and socially responsible practices
- Cybersecurity risks and technological challenges threaten data security and demand continuous innovation and investment
How can technology help optimize global supply chain networks?
Technology can enhance global supply chain networks by improving visibility, efficiency, and resilience. Technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, advanced analytics, and 3D printing enable:
- Localizing the production of goods.
- Tracking and tracing the movement of goods.
- Monitoring inventory levels.
- Analyzing real-time data.
- Automating warehouse operations.
- Improving delivery times.
- Proactively managing inventory.
- Optimizing strategic sourcing relationships.
- Creating new customer experiences.
What are the benefits of diversifying sourcing and production locations in global supply chains?
Diversifying sourcing and production locations can:
- Reduce the risk of disruptions.
- Increase business resilience and agility.
- Encourage innovation and sustainability.
- Ensure compliance with regulations and standards.
- Effectively manage costs and flexibility.
These benefits help companies navigate global market challenges and uncertainties, gaining a competitive edge.
What are the best practices for fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement in global supply chains?
To foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement, consider:
Embracing a learning and continuous improvement culture, empowering employees to challenge the status quo, experiment with new approaches, and learn from failures.
Developing open and transparent communication and cross-functional relationships to share ideas, feedback, and best practices.
Leveraging technology to optimize workflows, reduce waste, and enhance quality and flexibility.
What is a Supply Chain Strategy?
A supply chain strategy is a plan or approach businesses use to ensure that their supply chain operations are efficient, cost-effective, and capable of meeting customer demand. It involves the management of resources, processes, and relationships with suppliers and customers to achieve a competitive advantage.
How can businesses handle Supply Chain Disruptions?
Supply chain disruptions can be managed by implementing risk mitigation strategies such as diversifying suppliers, maintaining safety stock, investing in technology for real-time visibility, and developing a resilient supply chain. These measures help businesses quickly adapt to unexpected changes and minimize impacts on operations.
What makes a Supply Chain Resilient?
A resilient supply chain is designed to withstand and quickly recover from disruptions. Key features include flexibility, redundancy, and anticipating potential risks. Investing in technology for better visibility, diversifying suppliers, and robust planning are crucial for building resilience.
What is involved in Supply Chain Planning?
Supply chain planning involves forecasting demand, managing inventory levels, coordinating production schedules, and ensuring the timely delivery of products to customers. It aims to balance supply with demand, optimize resource use, and minimize costs while meeting customer requirements.
What are common Supply Chain Challenges?
Typical supply chain challenges include managing supply chain disruptions, dealing with fluctuating customer demand, ensuring accurate supply chain data, and adapting to market changes. Supply chain managers must address these issues through effective planning and agile strategies.
How does Digital Transformation impact Supply Chains?
Digital supply chain transformations involve integrating advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain into supply chain operations. This digitalization enhances visibility, improves efficiency, and enables an agile supply chain to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands.