International geocoding



What is geocoding?
Granularity up to address level
Coordinates for UNLOCODEs
SOLUTIONS
Typical use cases for international geocoding
Overcome the challenges of international geocoding
Limited coverage
Unreliable sources
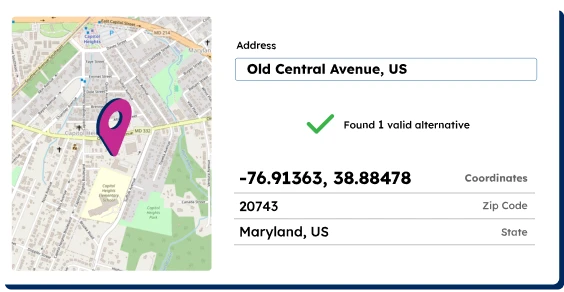
Poor data quality
Low match rate
Multiple address formats
MAIN FEATURES
Global coverage with local precision
High granularity
Our database enables accurate geocoding of zip codes, regions, cities, streets, and UNLOCODEs.
Global coverage
Reliable and up-to-date data for geocoding even in difficult geographies such as China, the UK, Russia, or Brazil.
247 countries in a standardized database
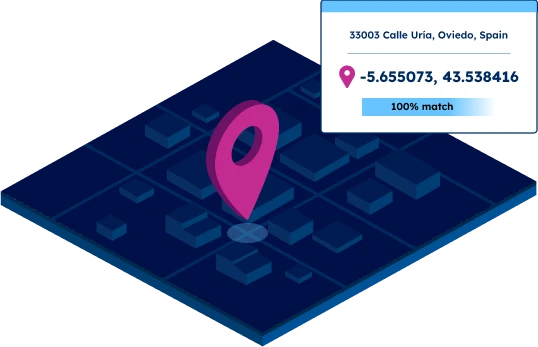
Unmatched data accuracy
Our advanced data pipelines capture, clean, format, and integrate new data on a weekly basis. Our proprietary data-mastering processes guarantee reliable coordinates at any level of precision.

“While using publicly available data for geocoding addresses, we realized that data coverage and quality issues were holding us back. We needed a consistent and standardized solution with global coverage. GeoPostcodes data has made a huge difference in our ability to reliably geocode and resolve addresses.”
David Henslovitz
Data Scientist at Everstream Analytics

"GeoPostcodes’ postal database, enhanced with high-resolution latitude and longitude geolocation, provides us with precise location data. This level of accuracy is essential for calculating mileage and CO2 emissions accurately, especially for road and truck transport."
Dr. Peter Wild
Managing Partner at CarbonCare

Self-hosted data
Get our geocoding data into your IT infrastructure. No need to set up, audit, and maintain a connection to a third-party service. Perfect for use cases that require big amounts of requests.
Rich attributes
Our geocoding data can be enriched with country-specific information, population, multi-language support, UNLOCODE, IATA codes, and time zones. Perform dynamic visualizations and geospatial analysis based on your specific needs.
Unique expertise
Our team has 15 years of experience in Enterprise integration with an in-depth knowledge of each country's postal structure.
Reduce integration time by 30%

WHY GEOPOSTCODES
Why rely on our international geocoding database?
High-quality data for geocoding
Highest quality
- Advanced geocoding
- 247 countries
- Weekly updates
Enterprise Grade Service
- 100+ successful integrations
- Dedicated Customer Success Manager
- Self-hosted
Plug and Play Design
- Seamless integration
- 299 languages
- Standardized and unified data structure
Our international geocoding articles
Frequently Asked Questions
Geocoding is the process of converting address data into geographic coordinates.
This process often starts with address validation, which ensures the accuracy of postal addresses or street addresses before they are geocoded.
Address validation checks if an address exists and corrects any formatting issues.
Once validated, geocoding services can accurately convert these addresses into precise latitude and longitude coordinates, enabling various applications from mapping to spatial analysis.
Batch geocoding is a method used to geocode addresses in large quantities.
Instead of processing addresses one by one, batch geocoding allows you to submit multiple addresses simultaneously.
This is particularly useful when dealing with extensive address data sets. The system processes these addresses in bulk, converting each one into geographic coordinates.
This method is highly efficient for tasks that involve geocoding a large number of postal addresses or street addresses at once, such as in market analysis or logistics planning.
Geocoding is fundamental to mapping applications like Google Maps.
When you input an address into Google Maps, the system uses geocoding to convert that address into geographic coordinates.
These coordinates are then used to place a marker on the map or provide directions.
Geocoding also enables features like finding the nearest street address to a given point.
While Google Maps is a well-known example, the principles of geocoding apply to various mapping and location-based services across different platforms.
Geocoding plays a crucial role in market analysis by adding a spatial dimension to data.
When business data is geocoded, it allows for powerful geographic analysis.
For example, by geocoding customer addresses, businesses can visualize customer distribution, optimize delivery routes, and make informed decisions about new location openings.
Geocoded data can be used to define sales territories, analyze competitor locations, and overlay demographic information for deeper market insights.
By converting address data into geographic coordinates, geocoding enables businesses to make data-driven decisions based on spatial relationships and patterns.
The accuracy of geocoding results can vary depending on several factors.
High-quality geocoding services strive to provide coordinates as close as possible to the actual location, often pinpointing the nearest street address.
However, accuracy can be affected by the quality and completeness of the input address data, the precision of the geocoding database, and the complexity of the address (e.g., rural vs. urban areas).
Some geocoding services can provide rooftop-level accuracy for many addresses, while others might only locate to the street or block level.
It’s important to note that geocoding accuracy can also vary internationally, as address systems and available data differ from country to country.
Geocoding is the process of converting addresses or place names into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). It allows you to pinpoint specific locations on a map.
Geolocation determines a device’s physical location, often using GPS or IP address. Geocoding converts addresses into geographic coordinates. Geolocation finds where something is, while geocoding translates descriptive location information into map coordinates.
The global geocode system, often referred to as the Geographic Coordinate System, uses latitude and longitude to specify locations on Earth. It provides a standardized way to represent any point on the globe using numerical coordinates.