Having up-to-date and standardized address data is key for providing quality services and products to our customers and stakeholders.
Whether for mailing, billing, shipping, or marketing purposes, having accurate address data ensures we can deliver exactly what they need.
Working with large address datasets has significant challenges, especially when managing a company that operates in multiple countries.
Different countries and regions have different formats and standards for postal addresses, and some international addresses may not even fit into a predefined schema.
This is where address standardization becomes essential. It helps adhere to each country’s local postal standards and improves data quality.
In this blog post, we will explore some of the challenges and solutions of Address Standardization.
What is Address Standardization?
Address standardization is about ensuring that addresses follow a consistent format that meets the rules set by the postal service in the specific country or region.
For example, the United States Postal Service (USPS) specifies rules for spelling, abbreviations, and formatting in the U.S.
Standardizing addresses enhances quality, accuracy, and deliverability, saving time and resources by minimizing errors, duplicates, and undeliverable mail.
The United States Postal Service (USPS) estimates that undelivered mail alone due to inaccurate address data costs US businesses a staggering $20 billion.
Understanding Address Standardization
Address standardization may involve modifying components, integrating missing data, or correcting inaccuracies. We can carry out this process manually or through software tools and APIs.
Software solutions speed up the process by using algorithms, which improve accuracy and efficiency.
However, the key part of Address standardization depends on having reliable address data. This is quite challenging when dealing with multiple countries’ address formats, given how often zip codes change, especially in large countries.
💡 Use accurate data for address validation. We update our location data weekly, relying on more than 1,500 sources. Learn more about address validation service and try a demo here.
Differences: Standardization, Validation, and Verification
Address Validation
Address validation verifies the existence and deliverability of an address against databases like GeoPostcodes.
When a customer enters their personal information, the system checks if the address they’ve entered exists. We can do this for just one address or a bunch of addresses at once.
This process is more complex than validation at the input, also known as auto-complete because the slightest difference in spelling will potentially flag an address as incorrect:

Address Verification
Address Verification confirms the association of an address with a specific individual or entity.
The process of verifying an address goes beyond validating that an address exists; it determines that an address is deliverable by comparing it against third-party reference data such as GeoPostcodes and involves address correction when possible.
For instance, on an e-commerce website’s checkout page, we might use address verification to ensure the address provided matches public records and belongs to the real person, preventing fraud.
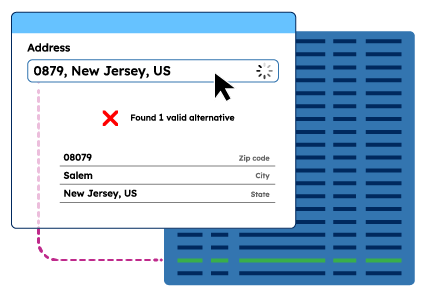
Address Standardization
Address standardization formats addresses according to standards, often relying on validation and verification processes.
An e-commerce company, for example, standardizes customer addresses in its database to ensure consistency and compliance with postal service formats, facilitating smooth shipping operations.
Common Terminologies and Standards to Standardize Address Data
CASS (Coding Accuracy Support System)
CASS is a USPS certification program assessing the precision and efficacy of address standardization software. A mailing house uses CASS-certified software to standardize and validate customer addresses, ensuring they meet USPS guidelines and qualify for bulk mailing discounts.
DPV – Delivery Point Validation
DPV confirms the existence and deliverability of specific addresses by appending a check digit to the ZIP+4 code. A utility company uses DPV to verify new customer addresses and ensure that service connections are only scheduled for valid and deliverable locations.
AFNOR – Association Française de Normalisation
AFNOR is the French standard for validating addresses, similar to the DPV system in the U.S. A French logistics company uses AFNOR standards to standardize and validate addresses for efficient delivery across France.
International Address Standardization
International address standardization tailors addresses from various countries or regions to a unified format, negotiating the myriad formatting rules and conventions distinct to each country or region.
A global e-commerce platform uses specialized software to standardize addresses from different countries, ensuring consistency and accuracy in international shipping.
Benefits of Address Standardization
Cost Savings and Reduced Return Rates
Standardizing addresses saves money by reducing returned or undeliverable mail costs.
For instance, a retailer that standardizes addresses in its database cuts undeliverable packages, saving on return shipping and improving delivery efficiency.
This method lowers expenses and streamlines operations, managing large datasets effectively.
Address standardization enhances operational efficiency and productivity.
By streamlining mailing and shipping processes through standardized addresses, a fulfillment center can sort and process deliveries more easily, speeding up delivery times and reducing errors.
Standardized addresses also enable seamless integration with various systems and applications, such as geographic information systems (GIS), customer relationship management (CRM), or marketing automation tools.
This integration allows for more refined data analysis, segmentation, targeting, and personalization, ultimately boosting business performance and outcomes.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Standardizing addresses is key to boosting customer satisfaction. It ensures deliveries are timely and accurate, which helps strengthen loyalty and engagement.
For example, a subscription box service that standardizes addresses ensures orders arrive promptly, increasing satisfaction and keeping customers coming back.
Accurate addresses also reduce the chance of wrong deliveries, improving the overall customer experience.
Address Parsing and Cleansing Methods
Parsing Methods
Parsing involves deconstructing an address into its essential components, such as street name, city, state, and ZIP code.
Scripts and APIs utilize algorithms and databases like GeoPostcodes to parse address data accurately.

Cleansing Methods
Cleansing addresses involves correcting errors or inconsistencies, such as duplicates, invalid entries, or outdated information.

This process includes several detailed steps:
- Data Import: Gather and import address data from various sources into a central system.
- Data Parsing: Use algorithms to parse address data, breaking it down into individual components like street address, ZIP code, and city.
- Data Standardization: Apply postal service rules to ensure consistency in formatting, incorporating address normalization to meet local postal standards.
- Data Validation: Verify addresses against authoritative databases to ensure accuracy, producing standardized address data that is reliable and up-to-date.
- Error Correction: Identify and correct inaccuracies, such as misspellings or incorrect ZIP codes, ensuring the address information is correct.
- Duplicate Removal: Detect and eliminate duplicate addresses to maintain a clean database and ensure each address record is unique.
The process of standardization and address normalization ensures that all street addresses are accurate and conform to postal standards, facilitating efficient and error-free mail delivery.
For more detailed information on address cleansing, visit our blog on address cleansing.
We can also use business intelligence software like Tableau or Power BI to import, transform, and enrich address data.
These tools help improve data quality and give us insightful visualizations and reports for better decision-making.
Manual vs. Automated Standardization
Volume Considerations
The decision between manual and automated standardization methods hinges on several factors.
Automated methods suit large data volumes, while manual methods are better for smaller quantities.
For instance, a national retailer with millions of addresses might use automated standardization to handle the large volume efficiently. In contrast, a local boutique with a smaller customer base might manually standardize its addresses.
Complexity Considerations
Automated processing works best for complex, diverse datasets, while we can use manual processing for simpler data.
A healthcare provider dealing with complex and diverse patient addresses would benefit from automated processing, while a small business with straightforward data could manage manual standardization.
This approach ensures the data remains accurate and consistent across various use cases.
Accuracy Considerations
Automated standardization offers more consistent and reliable results compared to the error-prone manual process. This saves time and ensures that the data is always in the correct format.
Cost Considerations
Automated standardization is generally more cost-effective and efficient than the labor-intensive manual approach.
An enterprise might opt for automated standardization to save on labor costs and improve efficiency, while a startup with limited resources might start with manual methods.
By evaluating the business’s specific needs, companies can choose the most appropriate method for their address standardization process.
Benefits of Using Standardized Address Data

Standardized address data significantly boosts business efficiency and effectiveness. For example, it simplifies parsing and cleansing of address data, ensuring accuracy and proper formatting of components like street names, numbers, and ZIP codes.
This prevents duplicate records and inaccurate addresses, resulting in more reliable address information and enhanced business data quality.
Conclusion
Address standardization is vital for converting address data into a uniform format compliant with postal service rules.
This saves money, makes operations smoother, keeps customers happier, and ensures better data quality.
Use accurate data for address standardization to make sure operations run smoothly and customers are satisfied.
At GeoPostcodes, for over 15 years, we have created the most reliable and accurate Worldwide Address Database.
We update our location data weekly, relying on more than 1,500 sources. Browse GeoPostcodes datasets and download a free sample here.
FAQ
What does it mean to standardize an address?
To standardize an address means to convert it into a consistent format that adheres to specific postal guidelines.
This process involves correcting abbreviations, ensuring proper spelling, and reformatting the address elements (e.g., street number, street name, city, state, and ZIP code) according to the standards set by the postal authority.
Standardizing addresses ensures accuracy, improves deliverability, and minimizes errors in mailing and shipping operations.
What is the USPS address standardization system?
The USPS address standardization system involves converting addresses to the USPS’s preferred format.
This system uses the Coding Accuracy Support System (CASS) to evaluate and certify the accuracy of address standardization software.
CASS-certified software ensures that addresses are properly formatted, validated against the USPS database, and corrected if necessary.
This process improves mail delivery efficiency, reduces the number of undeliverable items, and qualifies mailers for postal discounts.
Why can’t an address be standardized?
An address might not be standardized due to several reasons:
- Incomplete Information: Missing essential elements such as street number, street name, or ZIP code.
- Invalid Information: Addresses that do not exist or contain fictitious elements.
- Incorrect Formatting: Addresses that do not follow the postal authority’s guidelines, including incorrect abbreviations or misspellings.
- Database Limitations: The address may not be listed in the postal authority’s database, especially if it is new construction or located in a remote area.
Standardization tools rely on accurate and comprehensive databases to validate and correct addresses.
If the input data is flawed or the database lacks the necessary information, the address cannot be standardized effectively.
What is the standard format of an address?
The standard format of an address varies by country but generally includes the following elements:
Recipient Name: The name of the person or organization.
Street Address: Includes the street number and street name.
City: The city or town name.
State or Province: The state or province code or name.
Postal Code: The ZIP code or postal code.
Country: The country name, especially for international mail.
For example, the USPS standard format for a U.S. address is:
John Doe
123 Main St
Springfield, IL 62701-1234
USA
This format ensures that all elements are present and correctly positioned, facilitating efficient mail processing and delivery.
For more detailed information on address formatting and standardization, visit our blog on address cleansing.



