Key Takeaways
- Geospatial data maps everything from roads to climate patterns
- Location intelligence turns geospatial data into actionable business insights
- Businesses use this insight to make strategic decisions in their operations
- Advanced GIS tools enhance the accuracy and depth of location-based analytics
Introduction to Location Intelligence
Location intelligence is all about turning geospatial data into actionable insights. You’ve probably seen location intelligence in action through maps, graphs, and charts that make complicated data easier to understand. It helps businesses spot patterns, predict trends, and answer location-based questions quickly.
But what exactly is geospatial data? How can it be used to tackle challenging problems in different industries? And how can location intelligence software help you make the most of spatial analysis and visualization?
This article will dive into these topics, showing how location intelligence can boost business operations.
💡 Use accurate location data to make smarter business decisions. For over 15 years, we have created the most comprehensive worldwide zip code database. Browse GeoPostcodes datasets and download a free sample here.
The Essence of Location Intelligence
Location Intelligence (LI) answers questions like:
- Where are my customers and competitors located?
- What are the best locations for my business?
- How can I improve the efficiency of my supply chain and logistics?
- How can I predict future outcomes and scenarios based on location?
Geospatial Data: The Foundation of Location Intelligence
Geospatial data is the backbone of location intelligence, giving us the crucial information needed to map and analyze physical spaces. This data isn’t just about coordinates; it includes a range of attributes that describe the location and characteristics of objects on Earth. It comes in two main types: vector data and raster data.
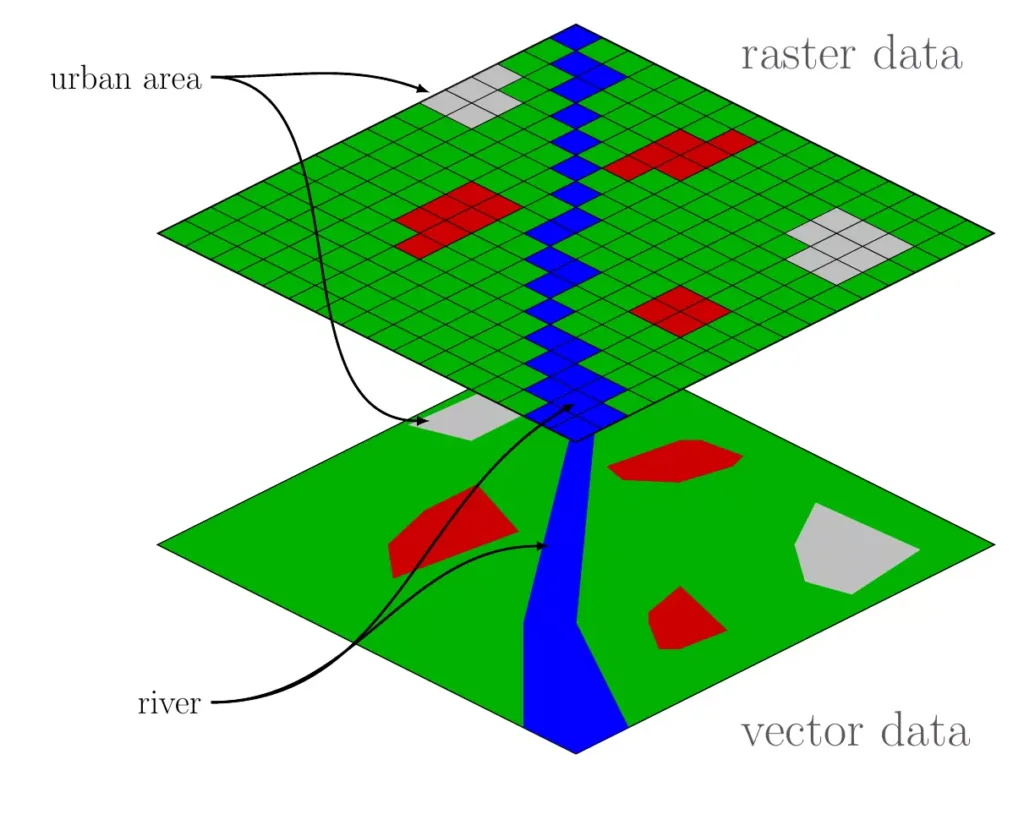
Vector Data
Vector data represents objects and features on Earth’s Surface, like roads, buildings, and landmarks. It uses points, lines, and polygons, each with precise geographic coordinates. A vector dataset of a city’s infrastructure might include points for fire hydrants, lines for streets, and polygons for parks and property boundaries. This data type is precise and perfect for applications that need detailed mapping and spatial analysis.
GeoPostcodes boundaries database, for instance, is delivered as vector postal boundaries. These boundaries outline the specific areas covered by different postal codes.
The dataset comes from a topological model, ensuring that adjacent polygons (areas next to each other) perfectly match up with shared boundaries. It means no gaps or overlaps, guaranteeing accuracy in defining postal regions.
Below is an example of postal boundaries for China:
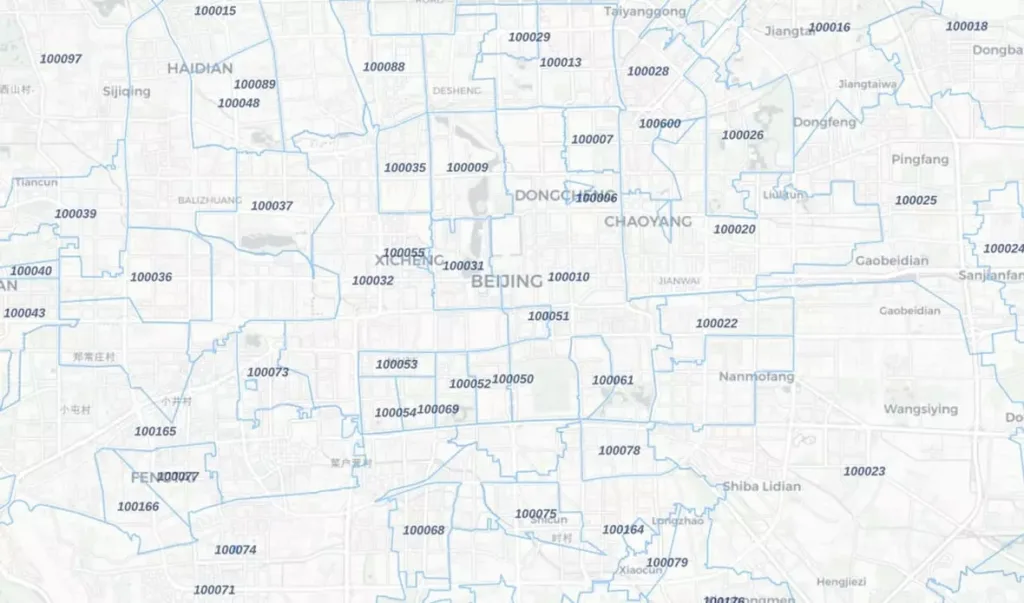
🌎 Searching for accurate China zip code format? Download our China zip code sample dataset here.
Raster Data
Raster data represents continuous phenomena. It consists of a grid of cells, each with a value for a specific geographic attribute like elevation, temperature, or land cover. Familiar raster data sources include satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and digital elevation models. This data type is beneficial for analyzing environmental factors and large-scale geographic trends, like climate patterns or vegetation health.
Accurately collecting and managing this data is crucial because it forms the basis for all subsequent analysis and visualization in LI. Tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) like ArcGIS are essential here. They help store, manipulate, and analyze location data effectively.
In our guide on Improving Business Operations with Location Data Accuracy, you can find detailed information about where location data comes from and best practices for managing it.
From Data to Decision: Analytical Processes in LI
Turning raw location data into actionable insights involves several key steps:
Data Preprocessing
During data preprocessing, we clean the data to ensure it’s accurate and ready for analysis. It might include geocoding (turning addresses into geographic coordinates) or reverse geocoding (turning coordinates back into addresses).
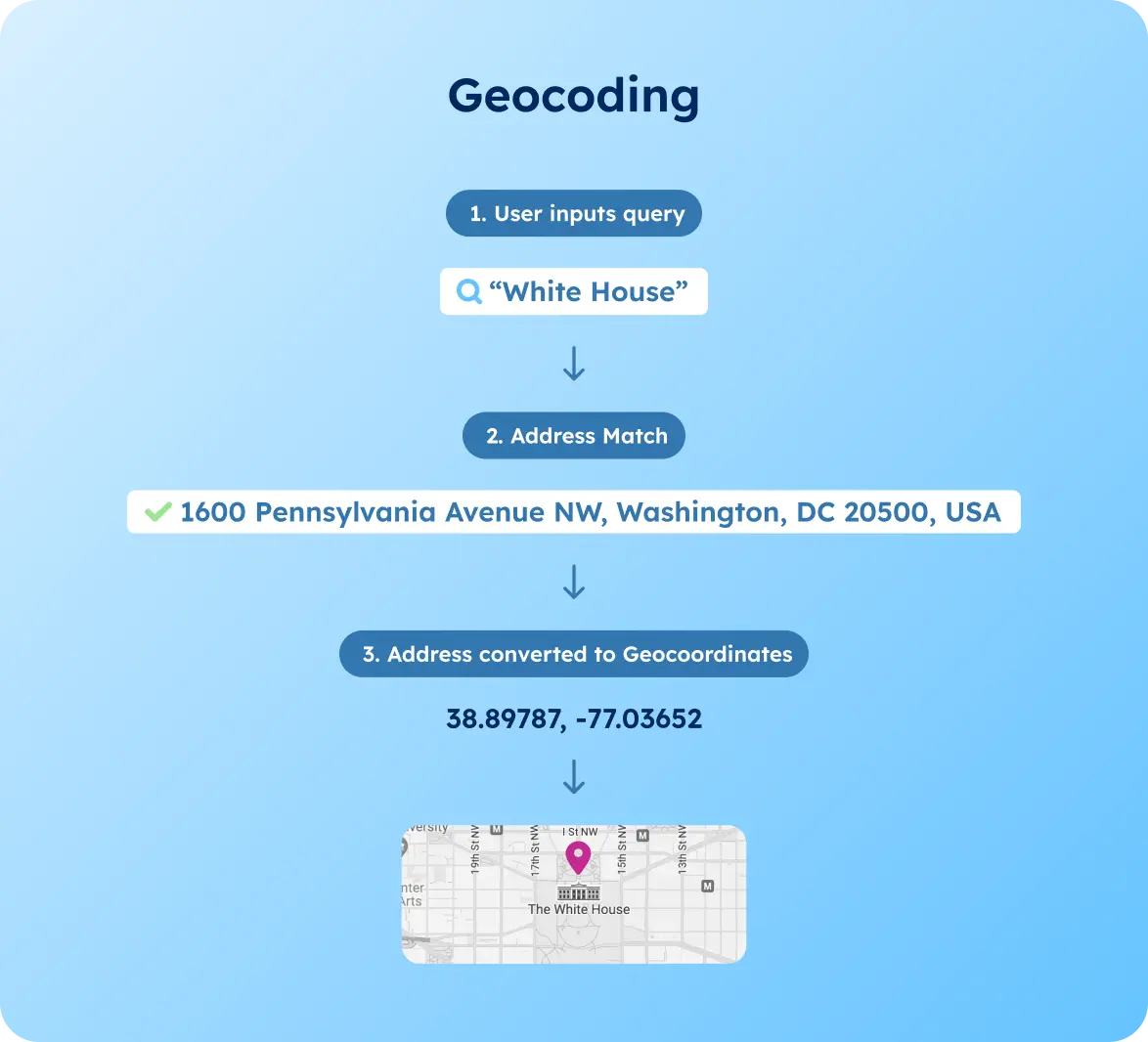
Please review our guides about Geocoding: Building a Zip Code Coordinates Converter and Geocoding: Building a Postcode to Coordinates Converter to learn how to use geocoding in different business scenarios.
Spatial Analysis
Using GIS tools can identify data relationships, patterns, and trends. Techniques like buffering, overlay analysis, and spatial clustering help us understand spatial dynamics. To know which tools are best for spatial analysis, check our guide on Comparing Zip Code Mapping Tools.
Below is an example of the spatial analysis software ArcGIS:
Predictive Modeling
Here, we apply statistical methods and machine learning algorithms to predict future trends based on historical data.
Visualizing Insights: Maps and Beyond
Visualization is a vital part of Location Intelligence. It turns complex data analysis into understandable, actionable formats. For example, you can create a zip code map to get actionable insights on marketing and sales territory planning, logistics and distribution management, and urban planning.
For example, below is London population data mapped by postcode:
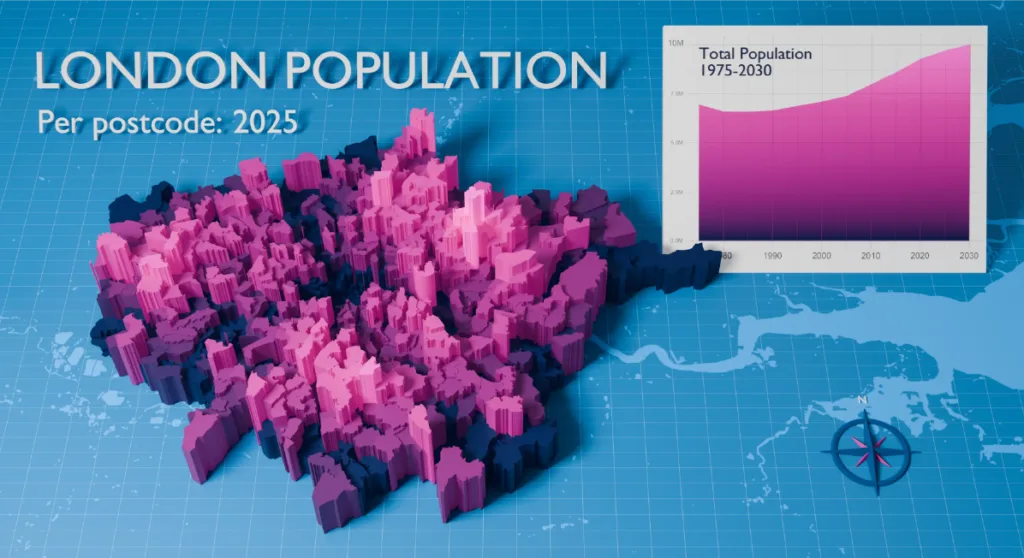
Advanced GIS software allows for interactive maps where users can zoom, pan, and click for more details.
Heatmaps can show the intensity of a phenomenon at different locations, and 3D models provide an immersive view of geographic data. Dashboards integrating maps with charts and graphs offer a comprehensive view, making data interpretation and decision-making faster and more straightforward.
Location Intelligence vs. Business Intelligence: Understanding the Differences
Business Intelligence (BI)
BI involves collecting, analyzing, and reporting data to help make better decisions. It allows companies to understand their performance, spot opportunities, and solve problems.
Location Intelligence (LI)
LI is a specialized part of BI that focuses on the spatial aspects of data. It helps companies see how location and geography impact their operations. LI enhances BI by adding context, depth, and precision, enabling analysis and visualizations that traditional BI tools cannot match.
Applications of Location Intelligence
This section will dive into how Location Intelligence is used in these areas.
Business Operations and Marketing Strategies
Location Intelligence helps businesses improve their strategies and operations by offering insights into customer behavior, market trends, competitor activities, and supply chain efficiencies. Here is how it can benefit your business:
Choosing Prime Locations
Using sales territory mapping software and GeoPostcodes data, you can analyze population density, income levels, traffic patterns, and consumer preferences to find the best spots for new stores, offices, or warehouses.
GeoPostcodes data offers precise and accurate data for territory mapping, primarily if your sales coverage is based on local divisions like postal codes. Browse our datasets and download a free sample here.
The analysis will also enable your business to offer personalized deals and services based on customers’ locations and preferences, boosting loyalty and targeting the most profitable customers. It will drive sales and revenue.
Optimizing Operations
Using accurate zip code data in logistics operations, you can calculate distance to estimate your cost, CO2 emissions, and other outputs. It will help you streamline routes, schedules, and inventory levels, cut costs, and minimize risks.
Check out our supply chain network design guide to discover the best practices for enhancing your logistics.
Urban Planning and Environmental Management
Location Intelligence helps urban planners and environmental managers create sustainable, livable cities by offering insights into the spatial patterns, trends, and impacts of human and natural activities. Here, it can benefit urban planning and environmental management:
- Developing Smart Cities: Use location data and technology to build intelligent communities that improve citizens quality of life, efficiency, and safety
- Monitoring Environmental Conditions: Track and analyze air and water quality, climate changes, and natural disasters
- Conserving Natural Resources: Precisely map the locations, significance, and vulnerabilities of natural resources and ecosystems to protect and rejuvenate them
Emergency Response and Public Safety
Location Intelligence is a game-changer for emergency responders and public safety officials. It provides real-time awareness, coordination, and communication, helping them prepare for and manage emergencies. Here are examples of how it makes a difference:
- Spotting Potential Hazards: Identify and evaluate risks like fires, floods, earthquakes, and terrorist acts, for example, mapping natural hazard risk areas to postal boundaries and points
- Timely Alerts: Deliver precise information and instructions to the public and media through location-based alerts and notification
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ve discussed location intelligence and how it helps choose prime locations, visualize complex data through maps and heatmaps, and provide real-time awareness for emergency responders.
With over 15 years of experience and weekly updates from over 1,500 sources, GeoPostcodes is your go-to partner for reliable geospatial data.
Download a free sample of our datasets and discover how accurate location data can elevate your business. Stay ahead of the competition with GeoPostcodes, your trusted partner in location intelligence.
FAQ
What is the difference between GIS and location intelligence?
GIS (Geographic Information System) is a technology for capturing, storing, and analyzing geographic data. Location intelligence builds on GIS by integrating this data with business analytics to provide actionable insights for decision-making.
What are the benefits of location intelligence?
- Enhanced decision-making
- Improved customer targeting
- Optimized logistics and operations
- Better risk management
- Increased market understanding
What is the difference between location intelligence and business intelligence?
Business intelligence (BI) focuses on analyzing business data to inform decisions. Location intelligence (LI) incorporates geographic data into BI, providing spatial context to business analytics for deeper insights.
What is location intelligence, and why is it essential for businesses?
Location intelligence refers to location-based intelligence derived from geographical data. It helps businesses by providing insights into customer behavior, optimizing logistics, and improving decision-making processes.
This essential business intelligence tool enhances strategic planning and operational efficiency.
How do businesses use location intelligence data?
Businesses use location intelligence data to analyze patterns and trends related to geographical locations. It can involve location data analytics, which helps understand market demographics and customer preferences and optimize supply chains.
What are the common use cases of location intelligence?
Many location intelligence use cases include retail site selection, urban planning, logistics optimization, and disaster response planning. Using GIS software location intelligence, organizations can visualize and interpret spatial data effectively.
How can businesses expand their location intelligence solutions?
Businesses can expand location intelligence solutions if they integrate more comprehensive data sources and advanced analytical tools.
It includes using location data analytics and accessing accurate location data from providers like GeoPostcodes to enhance the accuracy and scope of their insights.
What type of data is essential for location intelligence?
Location data refers to any data with a geographical component, such as coordinates, addresses, or postal codes. High-quality data from providers like GeoPostcodes are crucial for accurate and reliable location intelligence.
How do GIS software and location intelligence work together?
GIS software location intelligence combines geographic data with sophisticated mapping and analysis tools.
This synergy allows businesses to access authoritative government data and other sources to create detailed maps and visualizations, supporting various operational and strategic needs.
How can businesses ensure efficient location intelligence access?
Businesses can ensure efficient location intelligence access by implementing robust data management systems and using reliable sources of geographic information.
It facilitates quick and easy access to critical location data for informed decision-making.



