Introduction
Shipping zones are a critical component of the ecommerce business and logistics ecosystem. These predefined geographical areas, established by carriers like USPS, FedEx, and UPS, help determine shipping costs and delivery times.
In the United States, shipping zones range from Zone 1, which is closest to the shipping origin, to Zone 8, the farthest. The farther the destination, the higher the shipping cost.
This zoning system ensures transparency for both shippers and customers, setting clear expectations for delivery times and costs and making precise zone calculations important for cost control and operational efficiency.
However, accurately mapping these zones requires a more granular approach. The key to accurate zone-based pricing and route planning lies in precise postal and ZIP code data. They are essential tools for businesses optimizing their shipping strategies.
💡 Use accurate location data to plan your route and calculate the shipping costs and time. Our worldwide ZIP code data is updated weekly, relying on over 1,500 sources. Browse GeoPostcodes datasets and download a free sample here.
In this guide, we will dive deep into the concept of shipping zones, exploring their definition, impact on shipping logistics, and how accurate location data can enhance your shipping strategy.
Understanding Shipping Zones
Definition and Purpose of Shipping Zones
Shipping zones are more than just geographical areas; they are a sophisticated system designed to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of shipping for both carriers and customers. Carriers use these areas to group destinations by distance from the shipment’s origin. This helps set standard prices and delivery times, ensuring reliable and consistent service.
Shipping zones help calculate shipping costs and predict delivery times. By dividing the country into zones, carriers create a tiered pricing model based on distance. This approach helps balance costs, improve efficiency, and offer competitive services.
Instead of fixed borders, zones use postal and ZIP code data for accurate rates. A clear zone structure optimizes resources and plan fulfillment strategies that reduce shipping costs and transit time.
Mapping the Zones
Mapping shipping zones is a thorough process that takes into account several critical aspects, including geographical boundaries, origin and destination points, and carrier-specific regulations. Prominent carriers such as USPS, FedEx, and UPS have crafted detailed zone maps that partition the country into multiple zones, each denoting a specific distance range from the shipping origin.
For example, the USPS shipping zones map is segmented into nine distinct zones, with Zone 1 encompassing areas within a 1 to 50 shipping zone mile radius from the shipping origin, and Zone 9 encompassing U.S. territories irrespective of distance. FedEx and UPS also have their own zone definitions, though they largely adhere to a similar pattern of increasing distance from the origin point.
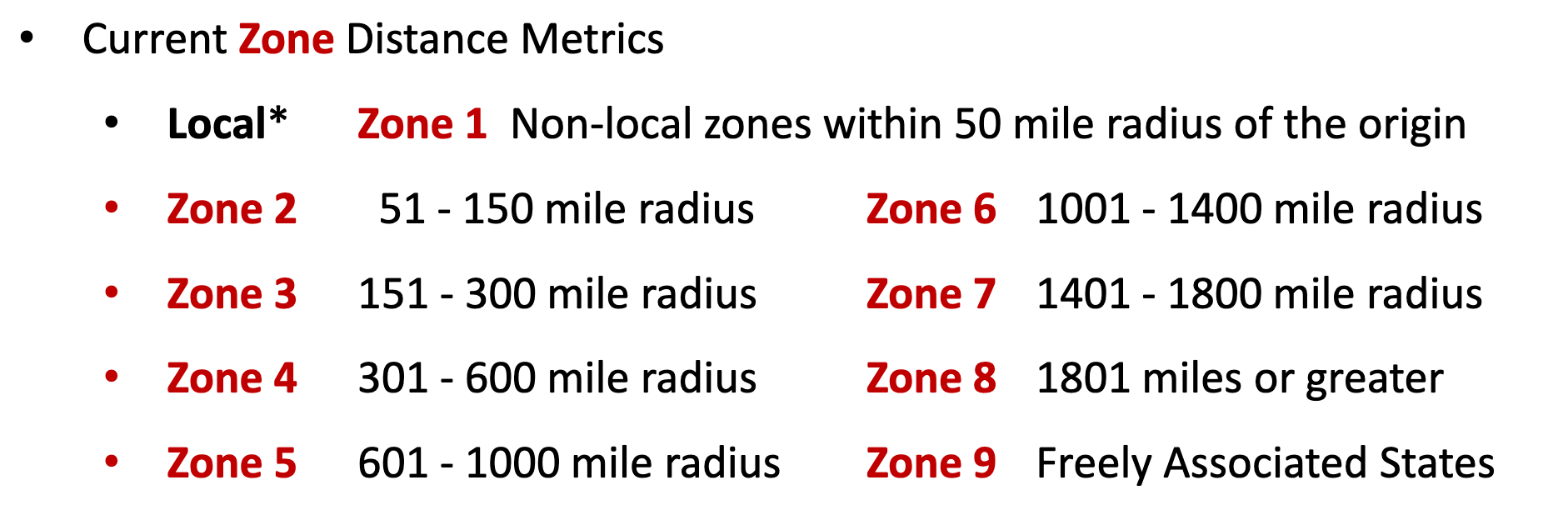
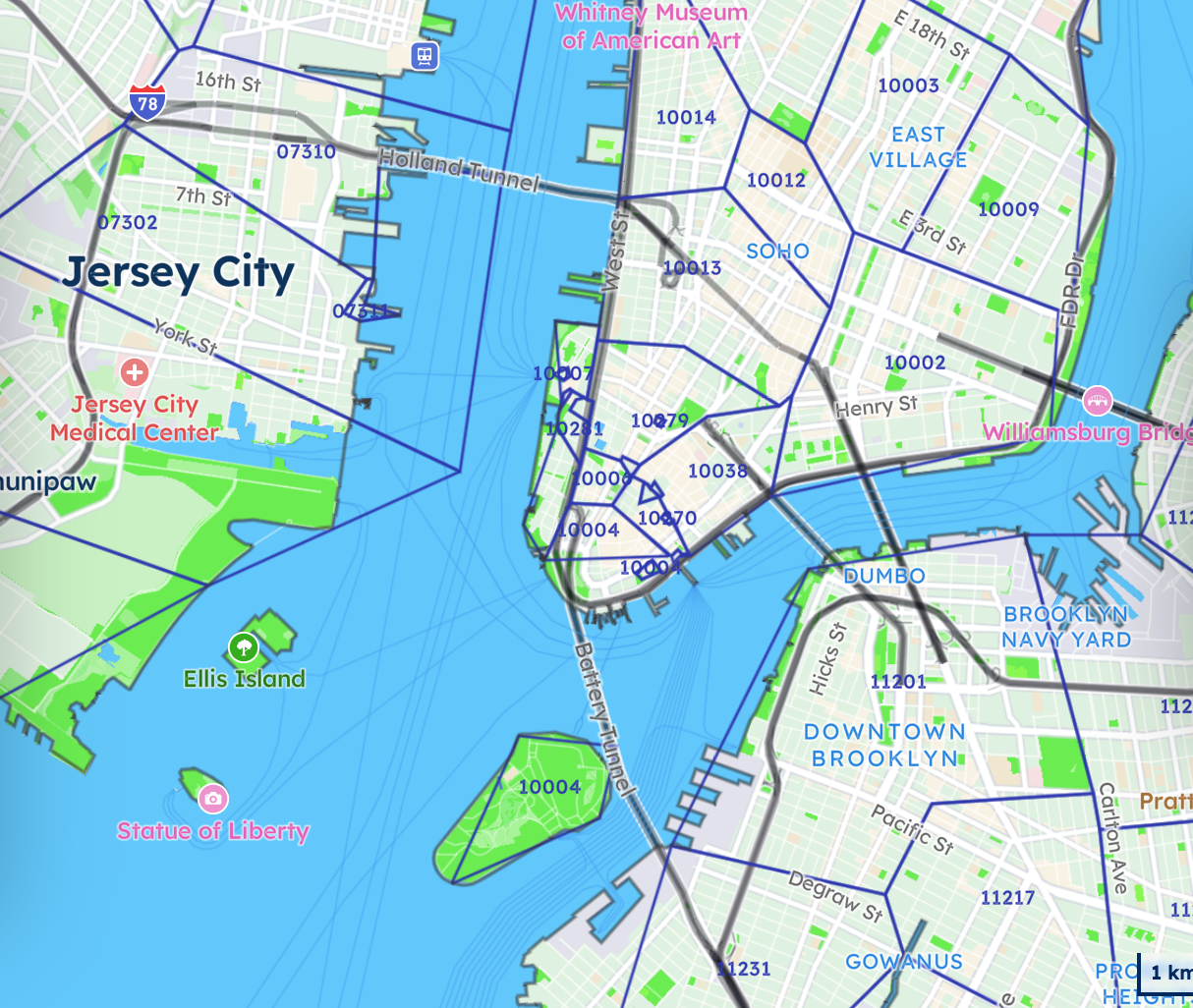
These zone maps frequently rely on ZIP code groupings, which aid in pinpointing the precise zone category for any given shipment. Utilizing tools provided by carriers, such as zone charts or online calculators, shippers can effortlessly determine shipping zones for their packages by entering the origin and destination ZIP codes.
The Role of ZIP Code Data
The accuracy of shipping zones depends on precise postal and ZIP code data. Carriers use detailed ZIP code boundaries to determine the exact location of shipping zones, making an up-to-date ZIP code database essential for businesses that rely on accurate cost projections and optimized logistics. Incorrect or outdated ZIP code information can lead to misclassified shipping zones, resulting in unexpected costs, delivery delays, or misrouted packages.
For companies handling high shipping volumes, leveraging a comprehensive postal data base ensures that shipping zones are applied correctly, improving cost efficiency and operational accuracy.
Impact of Shipping Zones on Costs
How Shipping Zones Affect Costs and the Importance of precise Postal Data
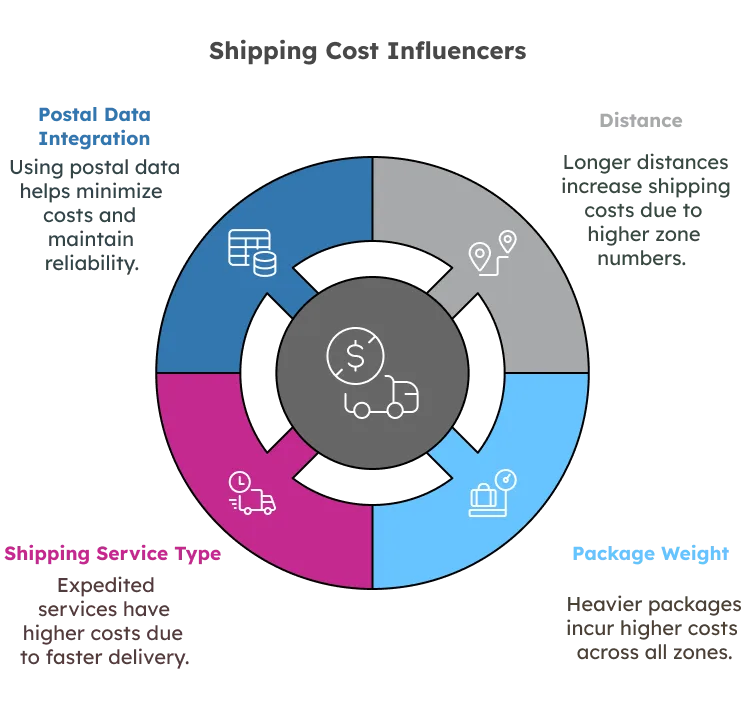
Shipping zones have a profound impact on the pricing of shipments, largely influenced by the distance a package travels. The further the destination from the origin, the higher the zone number, and, consequently, the higher the shipping costs.
This increase in cost is due to carriers incurring greater expenses for fuel, labor, and infrastructure as the distance extends.
Package weight is another key factor influencing shipping costs. Heavier packages typically incur higher costs across all zones, as they require more resources to transport. For example, shipping a 3-pound package from Zone 1 to Zone 8 is significantly more expensive than sending a 1-pound package the same distance. Carriers use weight brackets to structure pricing, with costs increasing progressively based on the combination of weight and distance.
In addition to distance and weight, the type of shipping service selected also affects pricing. Expedited services, such as USPS Priority Mail Express or FedEx Overnight, generally have higher costs due to faster delivery times and premium handling.
Businesses usually make more informed shipping decisions by integrating a comprehensive postal database into their logistics strategy, minimizing costs based on the ZIP code zones while maintaining reliable delivery times.
Calculating Shipping Costs Based on Zones
To calculate shipping costs based on zones, several key steps are required. Determining shipping zones is the first step, it is to say, you should identify the origin ZIP code and destination ZIP code. Most carriers provide zone charts or online calculators to assist in this process.
After identifying the shipping zone, you can use the carrier’s rate calculators to estimate the shipping cost. These calculators typically require the package’s weight, dimensions, and the chosen shipping method. FedEx and UPS, for instance, offer online tools that provide instant quotes based on this information.
Additionally, third-party logistics providers may offer their own cost calculators to help optimize shipping strategies.
However, businesses dealing with large shipment volumes sometimes need a more integrated approach. Leveraging a ZIP code and postal database enables companies to automate shipping cost calculations by directly mapping package destinations to their respective zones.
Businesses that work with third-party logistics providers or ecommerce platforms also need access to real-time postal data to ensure accurate rate calculations across different regions.
It’s also important to consider any additional services that may affect the final cost. Services such as insurance, tracking, and special handling can increase the overall cost of shipping. By including these elements in your calculation, you can obtain a comprehensive estimate of the total shipping cost.
Shipping Times and Zone Considerations
How Shipping Zones Influence Delivery Speed
Shipping zones play a critical role in determining how quickly packages reach their destination. The farther a package must travel across different zones, the longer the transit time.
Each shipping zone represents a specific distance range from the point of origin, directly influencing transit times. For example, USPS zone maps indicate that deliveries within Zone 1 can take as little as 1-3 days, while shipments to Zone 8 may take up to a week or longer, particularly during peak seasons.
Optimizing Fulfillment with Zone-Based Strategies
Additionally, the type of shipping service chosen also affects transit speeds. Expedited services such as USPS Priority Mail Express or FedEx Overnight prioritize shorter delivery times, but even these services are subject to distance-based constraints.
The efficiency of shipping zones is also determined by the availability of multiple fulfillment centers and how well a business can optimize its shipping operations.
For example, an ecommerce company with a single fulfillment center on the East Coast may struggle to provide fast and affordable shipping to customers on the West Coast because each package must cross multiple zones, driving up both transit times and costs. Expedited services like USPS Priority Mail Express can reduce delivery times, but the underlying zone structure remains a determining factor in overall efficiency.
By setting up additional fulfillment centers in key locations, businesses can significantly reduce the number of zones a package must travel through, resulting in shorter delivery times and lower costs.
Let’s look at a use case here: companies like ShipBob have successfully implemented this strategy by establishing multiple fulfillment hubs across the United States, allowing them to minimize higher-zone shipments and optimize transit efficiency. Having multiple distribution centers on the East Coast, West Coast, and Midwest can ensure that most shipments fall within lower zones, reducing costs while maintaining faster average delivery speeds.
The Role of Geospatial Data in Shipping Efficiency
The importance of precise postal data becomes even more evident in international shipping, where postal code boundaries directly influence delivery routes and costs.
Businesses managing global logistics require an up-to-date postal database to determine the most efficient shipping paths, ensuring accurate delivery estimates and avoiding delays due to misclassified zones.
Whether for domestic or international shipping, integrating high-quality ZIP code and boundary data enables businesses to optimize fulfillment strategies, reduce unnecessary costs, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grasping the concept of shipping zones is essential for any business engaged in order fulfillment. These zones, which classify destinations based on their proximity to the origin, have a profound effect on shipping costs, delivery times, and the overall efficiency of logistics.
The direct relationship between shipping zones and costs highlights the need for strategic warehouse placement. Businesses that integrate postal and boundary data can analyze customer locations, optimize distribution networks, and reduce high-zone shipments, ultimately lowering expenses and improving delivery speeds.
In addition to this, access to precise location data enables companies to refine their carrier selection, negotiate better rates, and ensure reliable delivery estimates for their customers. By adopting a data-driven approach and utilizing ZIP code and postal databases, businesses can enhance their shipping strategies, streamline logistics operations, and gain a competitive advantage.
To evaluate your shipping zones, implement location-based optimizations, and maximize efficiency in your supply chain, consider leveraging accurate and up-to-date location data from GeoPostcodes. This foundational data will ensure shipping efficiency. Ready to start your journey? Contact us today.
FAQ
What are the different zones for shipping?
Shipping zones are geographic regions measuring distance between origin and destination points. Most carriers divide the US into 8-9 zones, with Zone 1 being closest to the shipment origin and Zone 8/9 farthest. International shipping typically uses separate zone classifications based on country groupings.
What is zone 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 USPS?
USPS zones represent distance from origin: Zone 1 (local, 0-50 miles), Zone 2 (regional, 51-150 miles), Zone 3 (151-300 miles), Zone 4 (301-600 miles), and Zone 5 (601-1000 miles). These distance-based designations determine shipping rates and delivery timeframes for various USPS services.
How do I find my shipping zone?
Find your shipping zone using carrier zone calculators on USPS, UPS, or FedEx websites. Enter origin ZIP code (where you’re shipping from) and destination ZIP code to determine the applicable zone. Most e-commerce platforms and shipping software also provide automated zone calculations.
What does zone 1 and 2 mean in shipping?
In shipping, Zone 1 typically refers to local deliveries within approximately 0-50 miles from the origin point. Zone 2 covers regional destinations about 51-150 miles away. These closest zones generally offer the fastest delivery times and lowest shipping rates compared to higher-numbered zones.
How to calculate shipping zones, and what factors determine the zone number for a shipment?
Shipping zones are calculated based on the distance from the shipment’s origin to its destination, using ZIP code groupings defined by carriers. The zone number increases with the distance, with Zone 1 being the closest and higher zones indicating farther destinations.
Shipping carriers like USPS, UPS, and FedEx use zone maps and online calculators to determine these zones, which are essential for estimating shipping costs and delivery times.
Do carriers offer free shipping to all zones?
Free shipping availability depends on the shipping zone and the carrier’s policies.
Some regions may qualify for free shipping based on order value, membership status, or promotions.
What are rate cards?
A rate card standardizes shipping costs by outlining rates based on shipping zones, package weight, and delivery speed. For logistics companies, it ensures cost transparency, helps optimize route planning, and enables accurate pricing strategies to improve efficiency and profitability.