Key takeaways
- ZIP codes are specific to the US, while postcodes are used internationally, generally in English-speaking countries
- ZIP codes are five-digit numbers; postcodes can mix letters and numbers
- Different countries and even regions use distinct postal code formats
Introduction
Different countries have unique terms for their postal codes. For example, in the United States, they’re known as ZIP codes, an acronym for Zone Improvement Plan. In the United Kingdom and some other countries, they’re called postcodes. In this article, we’ll discover the differences between zip and postcodes.
Read “Zip Code Formats: A Global Guide to Accurate Postal Codes” to discover the format of postal codes in different countries.
💡 Navigating various postal code formats is challenging for global businesses. That is why, for over 15 years, GeoPostcodes has been providing the most comprehensive worldwide postal and zip code database. Explore our datasets and download a free sample here.
What is a Zip Code?
A zip code is a five-digit number that identifies a specific geographic region in the United States. It is a postal coding system utilized by the United States Postal Service (USPS).

The initial digit represents a broad geographic area, starting from 0 in the Northeast to 9 on the West Coast. The subsequent two digits pinpoint a regional area or a sectional center facility, essentially a key mail processing center. The final two digits designate the specific local post office or delivery zone.
What is a Postcode?
A postcode is a sequence of letters, digits, or both, occasionally incorporating spaces or punctuation. Countries like the UK, Australia, and many others use the term postcode for their postal codes.
In the image below, you can see the UK postcode structure:
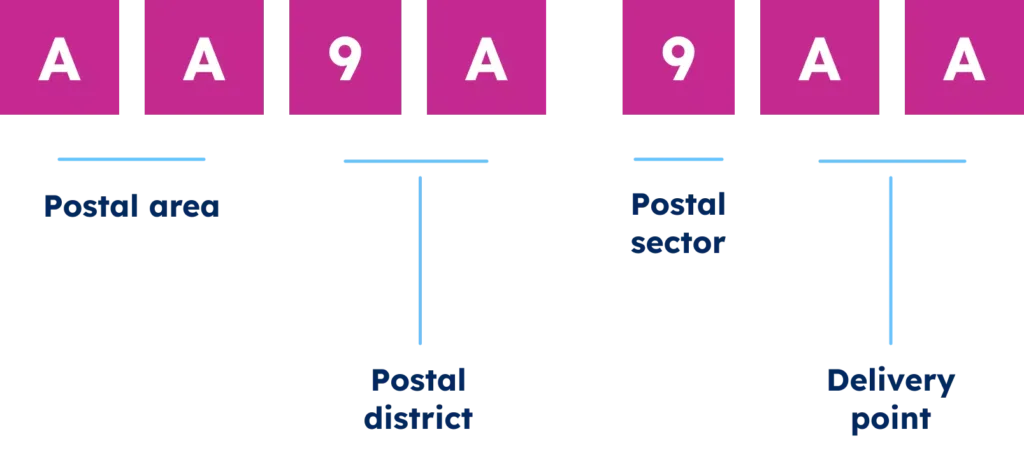
Differences Between Zip Code and Postcode
Geographical Use
The primary distinction between zip codes and postcodes lies in their geographical application. The term zip code is used explicitly in the United States, referring to their unique postal code system. So, zip codes are generally unique to the US.
Conversely, the term postcode is employed in other countries globally. In the United Kingdom, they’re formatted in two segments like ‘SW1A 1AA’. Australia has four-digit numeric codes; for example, ‘2000’ represents Sydney.
Structure and Format
Structure and format further differentiate zip codes from postcodes. Zip codes, which segment the country into smaller areas, consist solely of numbers. Typically, a zip code is five digits long, but an optional four-digit extension, ZIP+4, can be added to provide more specific location details.
Postcodes vary by country in terms of format and length. They can include a combination of letters and numbers and sometimes spaces or punctuation marks, spanning three to 10 characters. These codes often convey information such as the city, district, street, or building.
Business Applications of Zip Codes and Postcodes
Zip codes are critical elements for any international business because they are one of the most crucial touch points with customers.
It is important to remember that zip codes and postcodes are dynamic and subject to changes, additions, or deletions based on population shifts, geographical changes, or evolving mail delivery requirements. That is why businesses must ensure they have access to the most accurate and up-to-date zip code and postal database.
Review our article How Often Do Zip Codes Change to explore more about postal code dynamics.
Businesses utilize zip codes and postcodes for operational and strategic purposes, such as address autocomplete, reporting alignment, and distance calculation.
Below are examples of different scenarios in which businesses use postal code data.
Address autocomplete
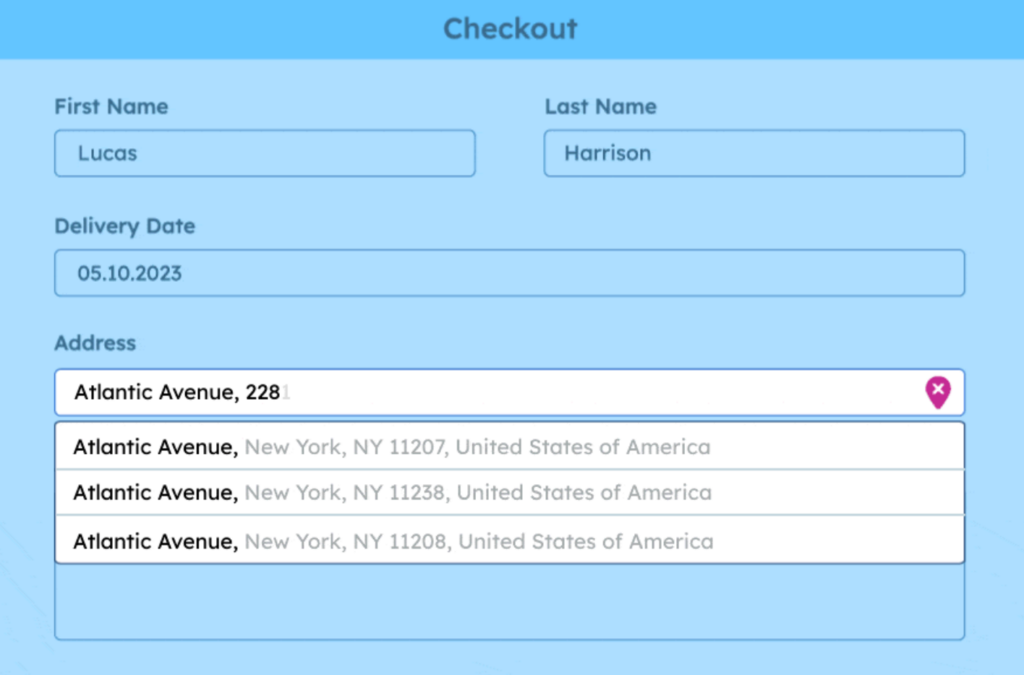
Address autocomplete is a feature that helps users quickly find and input accurate address information. When a user begins typing an address into a system, the system suggests valid options and corrects invalid entries. This autocomplete functionality can validate data at multiple levels—postal, street, locality, etc.—which ensures high data accuracy and user convenience.
Systems can validate whether the postal code exists, whether the street name is valid, and whether the locality matches the postal code. For instance, typing a postal code can automatically fill in the corresponding city name.
This feature improves data capture accuracy, reduces errors, and enhances user experience by preventing incorrect or incomplete addresses from entering the system.
Reporting Alignment
Reporting alignment involves standardizing and synchronizing location data across multiple sources to ensure consistency in reports and analytics.
Different departments within a company, such as marketing and sales, might use different standards or outdated postal codes. Standardizing address formats and using current postal code data helps integrate and compare data accurately.
Example: If the marketing team uses “B-1000” for Brussels city center while the sales team uses “B1000,” aligning these formats ensures both teams can combine their insights seamlessly.
This process helps businesses avoid discrepancies and maintain reliable data, improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
Distance calculation
Distance calculation determines the distance between two physical points based on their latitude and longitude. This capability is vital for several business applications:
- Shipping Distance Calculation: Logistics companies use distance calculations to estimate shipping costs, CO2 emissions, and delivery times. Understanding the distance between points A and B on a shipping route helps optimize logistics and reduce costs.
- Distance Between Supply and Demand: In location-driven marketplaces, such as job boards, calculating the distance between a job applicant’s residence and location helps match candidates with suitable opportunities. It ensures that job postings are relevant to applicants based on proximity.
- Ads Targeting: Businesses can use distance calculations to target advertisements to people located within a specific radius of a location, improving the relevance and effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
A relevant sub-scenario is the radius search, which involves identifying all points within a certain distance from a defined origin. For example, a restaurant app might show users all restaurants within a 0.5 KM radius of their current location. It helps businesses provide location-based services and offers to their customers effectively.
These applications highlight the importance of understanding and utilizing zip codes and postcodes to enhance business operations, improve data accuracy, and support strategic initiatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zip codes, specific to the United States, and postcodes, used globally, facilitate the sorting and delivery of mail by segmenting regions into manageable areas.
Beyond postal services, these codes are indispensable for business functions such as address autocomplete, reporting alignment, and distance calculation. These applications significantly enhance data accuracy, operational efficiency, and strategic decision-making, helping businesses optimize workflows and better serve customers.
As zip codes often change with population and geographical shifts, updating databases ensures businesses remain agile and effective in a constantly changing landscape.
GeoPostcodes maintains the most precise zip code database worldwide. Download a free sample of our zip code data.
FAQ
Is A Zip Code the same as a postcode?
No, a ZIP Code is used in the United States, while a postcode is used in other countries like the UK. Both serve the same purpose of identifying specific geographic regions for mail delivery.
What is the ZIP or postal code of the USA?
The United States uses ZIP Codes, which are five-digit numbers (e.g., 90210). Some areas also use ZIP+4 codes for more precise locations.
What is a postcode example?
A postcode example from the UK is SW1A 1AA, which corresponds to a location in London.
Are postal address and postal code the same?
No, a postal address includes the recipient’s name, street address, city, and postal code. In contrast, the postal code is a part of the address used to identify the specific area for mail delivery.
What purpose do zip codes serve?
Zip codes serve various business operations, enabling precise address capture, calculating distances, aligning reporting, supporting master data management, and facilitating geocoding and reverse geocoding for logistics and supply chain operations.
What does a zip code refer to?
A zip code refers to a series of numbers and letters assigned to a specific area. Postal services use zip codes to identify the destination of mail and parcels.
This system helps organize the delivery process by separating large geographic regions into manageable sections.
How do postal departments utilize alphanumeric codes?
Postal departments often use alphanumeric codes for international shipping and to further refine mail sorting processes. These codes combine letters and numbers to provide more precise location information, especially useful in densely populated areas or for identifying specific institutions or businesses.
How does the postal department deliver mail efficiently?
The postal department delivers mail efficiently by utilizing a structured system of postal codes, such as zip and postcodes.
These codes help segment regions into manageable areas, ensuring that mail is sorted accurately and promptly delivered to the correct destinations.



