Map data visualization at global scale
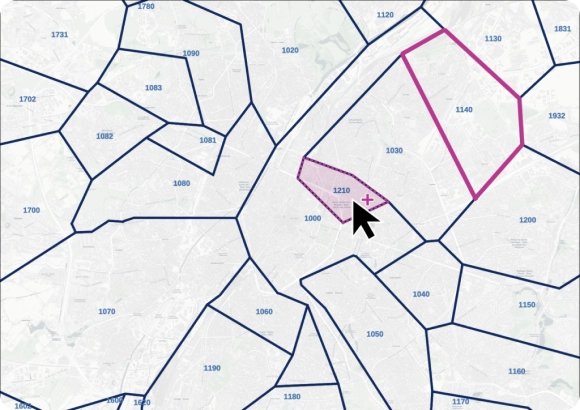
Granular data to build accurate maps at any level of precision


Map visualization in your software of choice
Our self-hosted database is standardized and pre-aggregated by zip code and administrative areas, making it ready to use in your visualization tools.







Data you can trust and rely on
Our advanced data pipelines capture, clean, format, and integrate new data on a weekly basis. Our proprietary data-mastering processes guarantee shape accuracy and reliable coordinates.
Trusted by Industry Leaders
Join more than 100 enterprise clients who trust GeoPostcodes for their location data
Anjo Grebe
Consultant


Dr. Peter Wild
Managing Partner

Kousha Mazloumi
Director of Data Science

Kousha Mazloumi
Director of Data Science

William Chao
Product Owner of Geographic Information Services


Kate Kilby
Senior Product Manager

Dave Hamm
Project Manager

Kavian Ranjbar
Data Governance Specialist

Nick Beaugié
Senior Software Engineer
Exert full control over your maps
Rich attributes
Understand the data behind your maps
Our team combines 15 years of experience in Enterprise geodata integration with an in-depth knowledge of each country’s postal structure.

Why choose GeoPostcodes
Global coverage
Complete coverage across 247 countries, including hard-to-source geographies like China, Japan, Brazil, and Russia.
Highest quality
Built on extensive, authoritative sourcing with robust data engineering and quality control. Standardized and up-to-date.
Expert Consulting
With 15 years of experience, we guide your implementation and deliver data in the format that fits your system.
Check our related map data visualization articles
Frequently Asked Questions
Map data visualization displays data on maps to analyze spatial relationships and patterns.
Geographic information system (GIS) technology transforms complex data into visual formats that are easily interpreted.
For example, visualizing population density or weather patterns on a map helps understand trends and make informed decisions.
Map visualization is crucial for several reasons:
Enhanced Understanding: It converts complex data into visual formats, making it easier to understand
Pattern Identification: It reveals trends and patterns that might be missed in traditional data formats
Improved Decision-Making: It supports strategic planning by providing clear, concise data representations
Effective Communication: Maps communicate information visually, making it accessible to a wider audience
For instance, businesses use map visualization for market analysis and urban planners for infrastructure development.
Using map visualization in Tableau involves these steps:
Connect Your Data: Import data into Tableau, ensuring it includes geographic fields like city names or coordinates
Create the Map: Drag geographic fields to the “Rows” and “Columns” shelves to generate a map
Customize the Map: Use the “Marks” card to adjust the data points’ colors, sizes, and details
Filter and Highlight: Apply filters to focus on specific areas or data points and use the “Highlight” function to emphasize them
Add Labels and Tooltips: Enhance the map with labels and tooltips for additional information on hover
Publish and Share: Publish the final map to the Tableau Server or Tableau Public for sharing
Presenting map data effectively involves:
Define the Purpose: Clearly outline the objective of your map
Choose the Right Map Type: Select a map type (e.g., heat map, choropleth map) that best fits your data
Prepare Your Data: Ensure data accuracy and proper geocoding
Design the Map: Focus on clarity, using intuitive colors and symbols
Add Labels and Legends: Provide clear labels and a legend for easy understanding
Use Interactive Elements: Add zoom, pan, and hover effects if possible
Include Contextual Information: Supplement the map with relevant charts or text
Test and Refine: Test with a sample audience and adjust based on feedback
Share Widely: Disseminate through reports, presentations, or online platforms
Interactive maps are dynamic maps that allow users to engage with the data in real time. Unlike static maps, these maps offer features like zooming, panning, and clicking on elements to retrieve more information.
They are important because they enable users to explore and analyze location data, understand spatial distribution, and interact with multiple layers of information.
This interactive nature helps make more informed decisions based on visualized geospatial data.
Interactive map tools effectively handle census data by visualizing demographic information across different geographic areas.
These tools can create various map types, such as heat maps and point maps, to represent the density and distribution of populations in a particular location.
By layering census data over a base map, users can explore patterns and trends in population dynamics, making it easier to understand and utilize this data for planning and analysis.
Geospatial data can create a custom map by integrating specific datasets relevant to the user’s needs. This data can include location data, spatial distribution, and other data from various sources.
Users can customize the map by using interactive maps and interactive map tools to display particular information, such as environmental data, traffic patterns, or business locations.
This customization allows for a tailored visualization that highlights specific insights and facilitates better decision-making.
Point maps are a type of map that uses points to represent specific data at particular geographic coordinates. These maps are particularly useful for visualizing location data such as addresses, event locations, or sensor data points.
By displaying data points on a map, users can easily see the spatial distribution of the data and identify patterns or clusters.
This visualization technique helps in understanding the geographic context and making data-driven decisions.
Heat maps are highly beneficial for representing geospatial data because they use color gradients to show the intensity of data values across a geographic area.
This type of visualization is particularly effective for highlighting areas with high or low concentrations of data points, making it easy to identify hotspots and trends.
Heat maps can visualize various data generated from social media check-ins, crime reports, or sales data, allowing users to grasp complex spatial patterns and make informed decisions quickly.
Different map types use various techniques to represent data, each serving unique purposes based on the kind of information being visualized.
For example, heat maps use color gradients to show the intensity of data values across a geographic area, making them ideal for highlighting hotspots and trends.
Point maps, on the other hand, use individual points to represent data at precise geographic coordinates. This method is useful for visualizing the distribution of locations such as stores, events, or sensor data.
Choropleth maps color-code predefined geographic areas to indicate different values or levels, and they are often used for demographic or statistical data representation.