Global location data for
logistics & shipping
Ensure every logistics workflow runs smoothly by powering address validation, tariff calculation, and customs operations with a reliable source of location data.


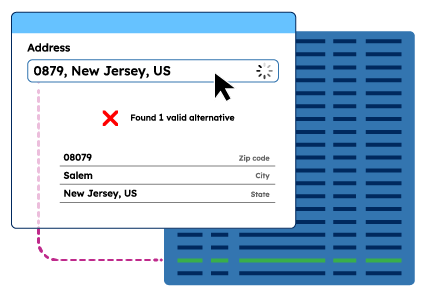
Enterprise Address Validation
CO2 calculation
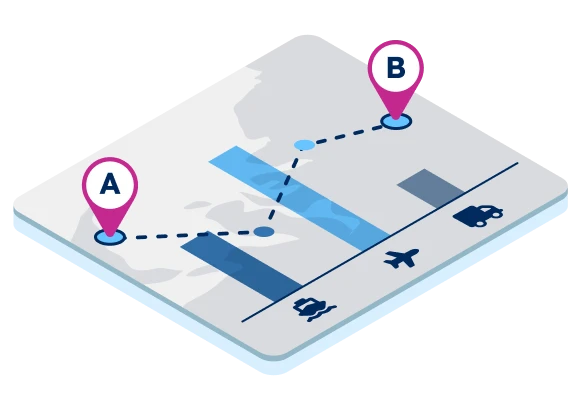
Map Visualization
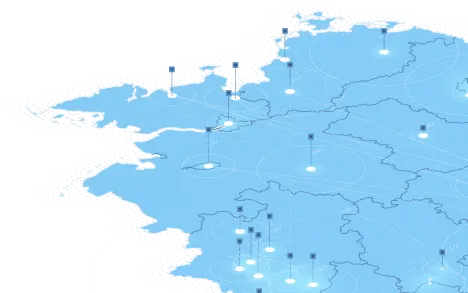
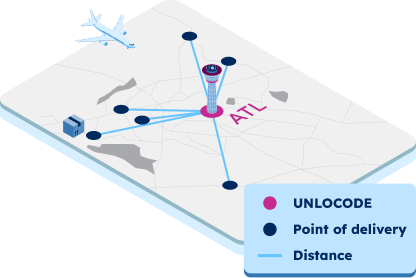
UNLOCODE and IATA codes
Trusted by industry leaders
Join more than 100 enterprise clients who trust GeoPostcodes for their location data
Anjo Grebe
Consultant


Dr. Peter Wild
Managing Partner

Kousha Mazloumi
Director of Data Science

Kousha Mazloumi
Director of Data Science

William Chao
Product Owner of Geographic Information Services


Kate Kilby
Senior Product Manager

Dave Hamm
Project Manager

Kavian Ranjbar
Data Governance Specialist

Nick Beaugié
Senior Software Engineer
Optimized ocean freight operations
Zone-based tariff calculation
Customs compliance

Network design & optimization
Why choose GeoPostcodes
Global coverage
Complete coverage across 247 countries, including hard-to-source geographies like China, Japan, Brazil, and Russia.
Highest quality
Built on extensive, authoritative sourcing with robust data engineering and quality control. Standardized and up-to-date.
Expert Consulting
With 15 years of experience, we guide your implementation and deliver data in the format that fits your system.
Our selection for Supply Chain and
Master Data Management
Frequently Asked Questions
GeoPostcodes supplies standardized location data for logistics and high-quality location data to help teams unify addresses, postal codes, and boundaries across supply chain management workflows. Using structured location data reduces inconsistencies and supports end-to-end supply chain visibility across markets.
Logistics companies rely on accurate location data and harmonized location data to reduce routing errors and validate geographic inputs. This accuracy strengthens supply chain operations, creating more reliable supply chain processes across regions and platforms. Learn more about how supply chain structures influence routing decisions in our guide to supply chain network design.
GeoPostcodes improves operational efficiency by delivering clean, standardized location data that reduces manual corrections in logistics operations. This streamlined data foundation supports enhanced operational efficiency, improves workflows, and contributes to stronger supply chain performance. Explore how accurate location data directly eliminates inefficiencies across logistics workflows.
Location intelligence helps organizations understand geographic structure, relationships, and boundaries by using comprehensive location data. This deeper visibility supports better planning in supply chain management, and applying location intelligence often helps teams optimize decisions across the entire supply chain.
Companies use real time location data to give context to movements and events in logistics operations. When real time location data is combined with stable location data, organizations maintain consistency and reduce errors across global supply chain networks. Real-time signals only work well when paired with a stable reference dataset that keeps all systems synchronized.
Teams use accurate location data and high-resolution location data to optimize routes, reduce travel time, and strengthen delivery predictability. When routing engines rely on validated location data, companies can optimize routes at scale and support healthier supply chain performance. Accurate ZIP code boundaries and geocodes help routing engines avoid misclassification and improve ETA precision.
Logistics companies use predictive analytics powered by standardized location data to forecast demand, plan capacity, and identify risks. Effective predictive analytics helps organizations build more resilient supply chain strategies supported by accurate geospatial inputs.
Reliable location data reduces address errors that often disrupt deliveries, contributing to higher customer satisfaction. When teams use harmonized location data, customer satisfaction improves due to fewer exceptions and better communication throughout the supply chain. High-quality datasets create smoother experiences, leading to consistently stronger customer satisfaction in logistics operations.
Growing logistics companies depend on structured location data and advanced location intelligence to expand into new markets without introducing inaccuracies. Global expansion requires adapting to postal systems that vary significantly by country, which makes standardized datasets essential. Using consistent location data keeps systems aligned and supports long-term supply chain scalability across borders.
GeoPostcodes provides continuously updated location data to reinforce supply chain management and long-term supply chain resilience. Reliable geographic information supports location intelligence, allows teams to optimize routes, and strengthens planning models such as predictive analytics, all while improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Consistent data across ERPs, TMS, and logistics platforms ensures systems continue to function smoothly as organizations scale.